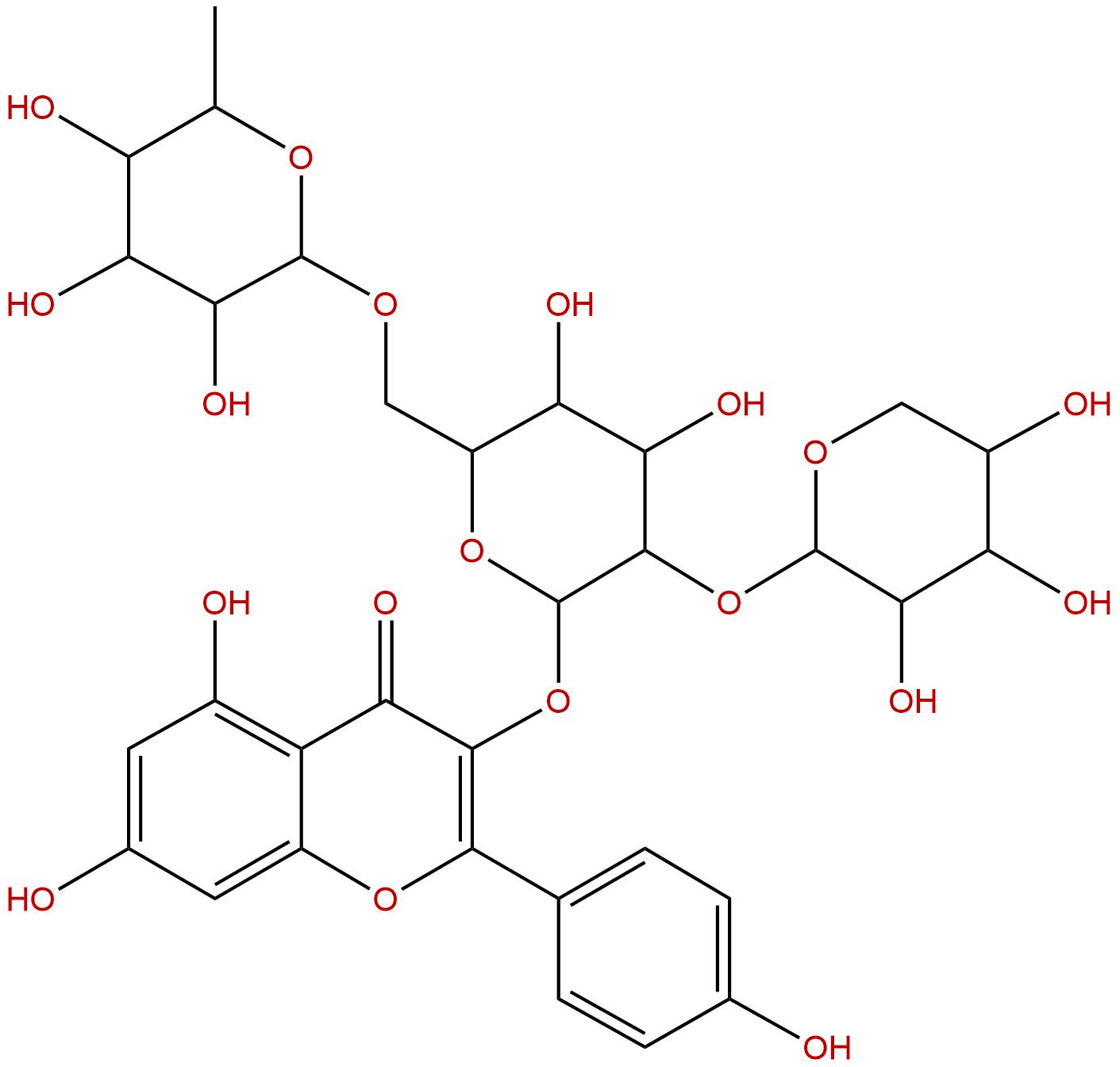
Camelliaside B Descrtption
Product name: Camelliaside B
Synonym name:
Catalogue No.: BP1471
Cas No.: 131573-90-5
Formula: C32H38O19
Mol Weight: 726.637
Botanical Source: Camellia oleifera Abel.
Physical Description:
Type of Compound: Flavonoids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams
Inquire for bulk scale.
Description:
Camelliaside B is a natural product from Camellia oleifera Abel.
References:
J Sci Food Agric. 2011 Oct;91(13):2315-21.
Isolation and anti-inflammatory effect of astragalin synthesized by enzymatic hydrolysis of tea seed extract.
The application of tea seed extract (TSE) has been widely investigated because of its biological activities. In this paper, two flavonol triglycosides in TSE-camelliaside A (CamA) and Camelliaside B(CamB)-were subjected to hydrolysis in the presence of two commercial enzyme complexes (Pectinex™ series): Smash and Mash.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Smash hydrolyzed only the xylosyl moiety of CamB, and the main product was kaempferol diglycoside (nicotiflorin, NF). On the other hand, Mash induced the hydrolysis of both CamA and CamB, and kaempferol monoglycoside (astragalin, AS) was found to be a main product. Pure AS with > 96% purity was prepared by enzymatic hydrolysis of TSE using Mash, and the chemical structure of AS was confirmed by (1)H- and (13)C-nuclear magnetic resonance analyses. The prepared pure AS showed anti-inflammatory activities by significantly inhibiting cellular nitrite oxide (IC(50) = 363 μg mL(-1)), prostaglandin E(2) (IC(50) = 134 μg mL(-1)) and interleukin-6 production (IC(50) = 289 μg mL(-1)) by lipopolysaccharide -stimulated RAW 264.7 cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
It was concluded that pure AS can be prepared by enzymatic partial hydrolysis of TSE and employed as an anti-inflammatory material. This is the first study to address the preparation of pure AS from natural sources.
HPLC of Camelliaside B