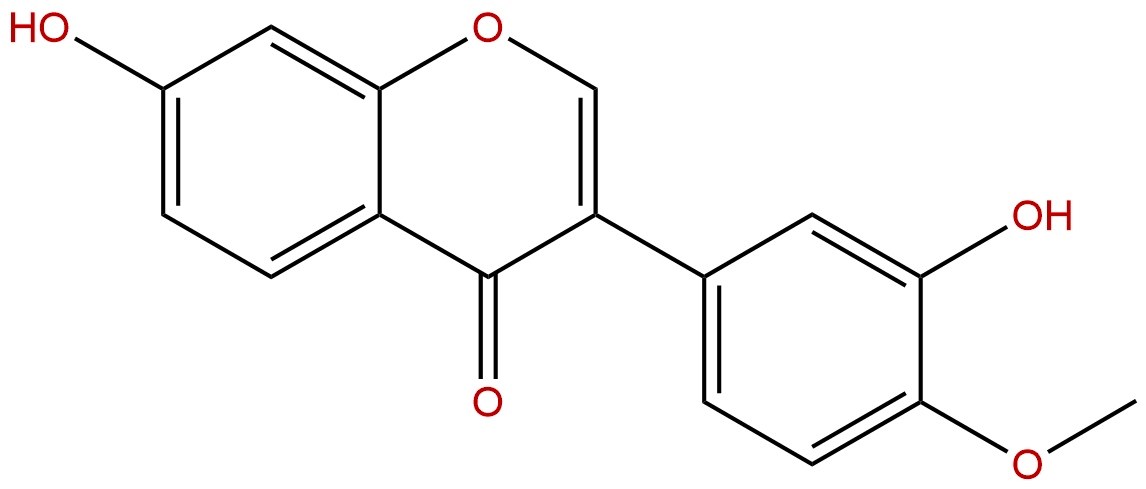
CalycosinCAS No.:20575-57-9
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0305 |
| Formula: | C16H12O5 |
| Mol Weight: | 284.267 |
Product name: Calycosin
Synonym name: 3′,7-Dihydroxy-4′-methoxyisoflavone; 3-Hydroxyformononetin; Cyclosin
Catalogue No.: BP0305
Cas No.: 20575-57-9
Formula: C16H12O5
Mol Weight: 284.267
Botanical Source: Baptisia, Bowdichia, Cadia, Cladrastis, Cyclolobium, Dalbergia, Machaerium, Myroxylon, Pterocarpus, Sophora, Thermopsis and Trifolium spp. (all Leguminosae subfamily Papilionoideae)
Physical Description: Yellow powder
Type of Compound: Flavonoids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams, up to kilograms
Inquire for bulk scale.
Descriptions:
Calycosin, a major isoflavonoid isolated from Radix Astragal, induces angiogenesis in human umbilical vein endothelial cell cultures (HUVEC) in vitro and zebrafish embryos in vivo via the up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), VEGFR1 and VEGFR2 mRNA expression;it acts similar to other selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) to promote angiogenesis via activation of MAPK with the involvement of ERK1/2 and ER. , such as raloxifene and tamoxifen, by displaying selective potency and affinity to estrogen receptors ERa and ERb.[1]
Calycosin has neuroprotective effects in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion rats, and the molecular mechanisms may correlate with the positive feedback between ER-α and miR-375, along with the regulation of downstream targets.[2]
Calycosin inhibits growth and induce apoptosis in ER-positive breast cancer cells, which is mediated by ER-α-induced inhibition of IGF-1R, along with the selective regulation of MAPK and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt pathways.[3]
Calycosin can promote proliferation of estrogen receptor-positive cells via estrogen receptors and ERK1/2 activation in vitro and in vivo.[4]
Calycosin can reduce advanced glycation end products-induced macrophage migration and adhesion to endothelial cells and relieve the local inflammation; furthermore, this effect is via estrogen receptor-ERK1/2–NF-κB pathway.[5]
Calycosin is a vasorelaxant, its action is endothelium-independent and is unrelated to intracellular Ca(2+) release; it is also a noncompetitive Ca(2+) channel blocker, the effect of it on Ca(2+) channel blockade may be different from that of dihydropyridines. [6]
References:
[1] Tang J Y, Li S, Li Z H, et al. Plos One, 2010, 5(7): e11822.
[2] Wang Y, Dong X, Li Z, et al. J the Neurol Sci, 2014, 339(2):144-8.
[3] Chen J, Hou R, Zhang X, et al. Plos One, 2014, 9(3):e91245.
[4] Chen J, Liu L, Hou R, et al. Cancer Lett, 2011, 308(2):144-51.
[5] Xu Y, Feng L, Wang S, et al. J Ethnopharmacol, 2011, 137(1):359-70.
[6] Xiu-li, Yin-ye, WANG, et al. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2006, 27(8):1007–12.
[7] Wang H, Yang L I, Fang L, et al. J Pharm Practice, 2015(01):53-4.
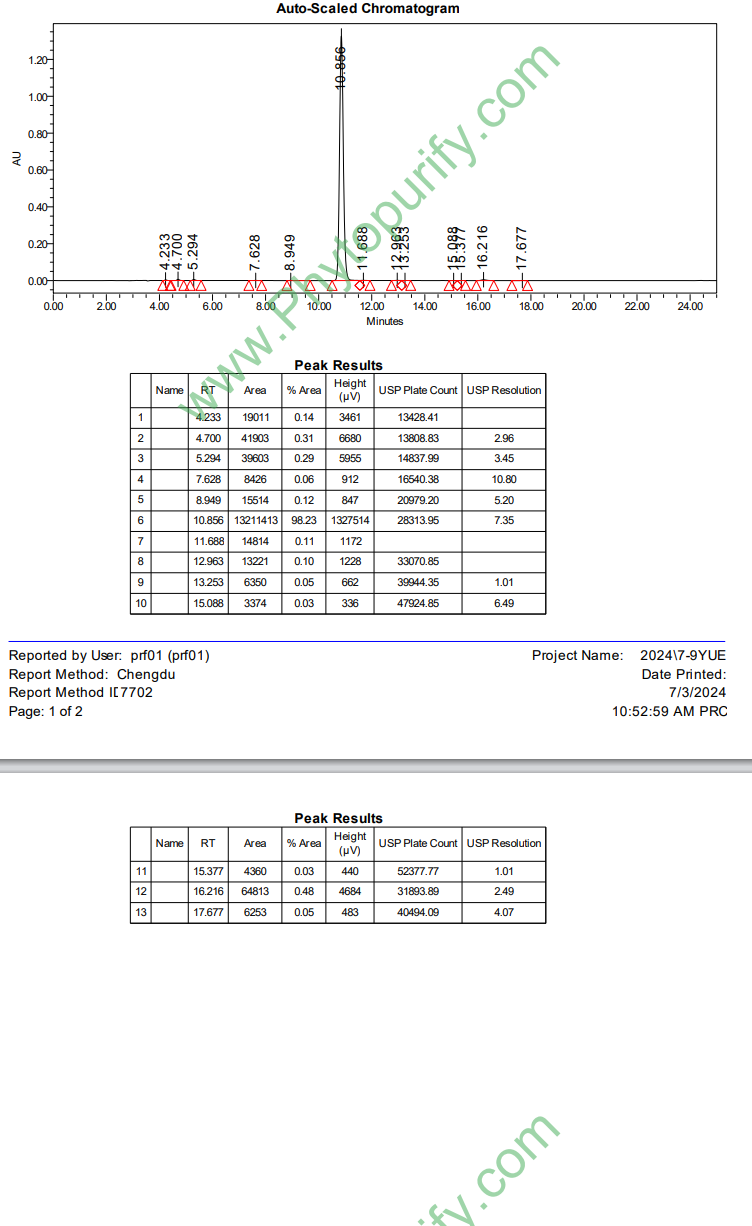
HPLC of Calycosin
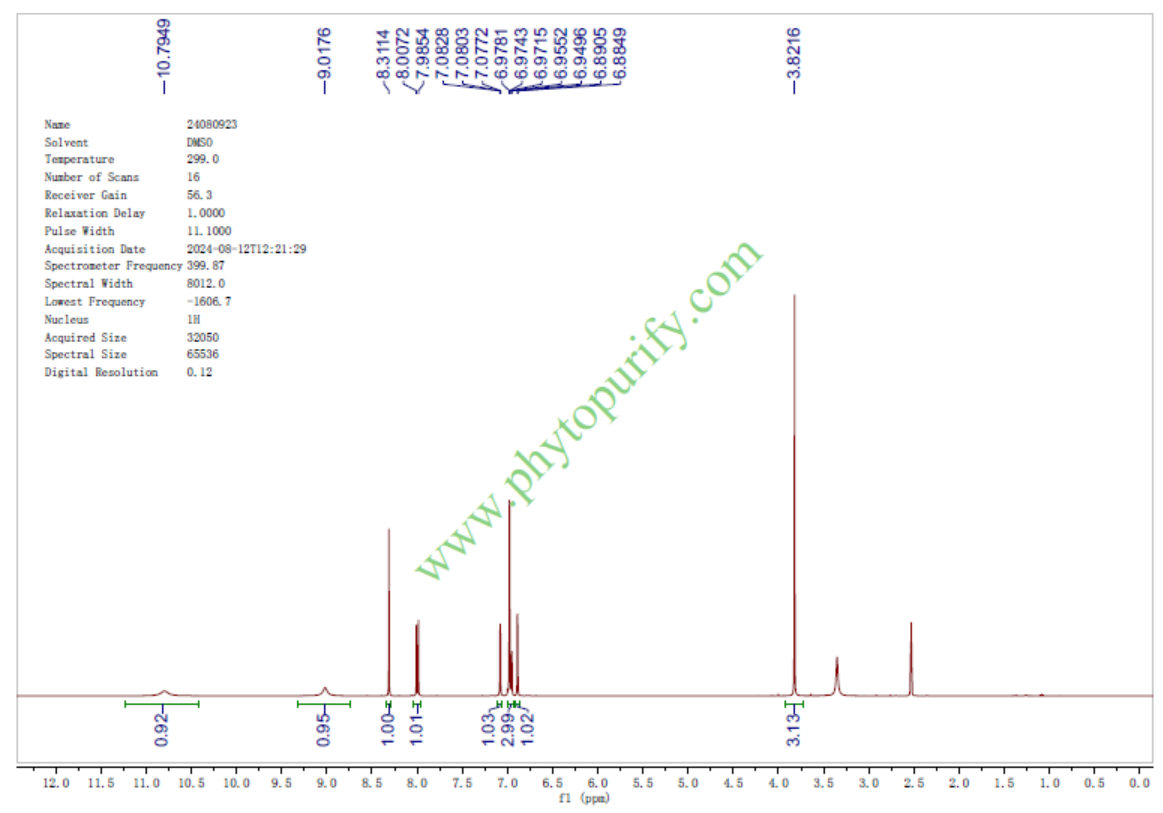
HNMR of Calycosin