
BisdemethoxycurcuminCAS No.:33171-05-0
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0278 |
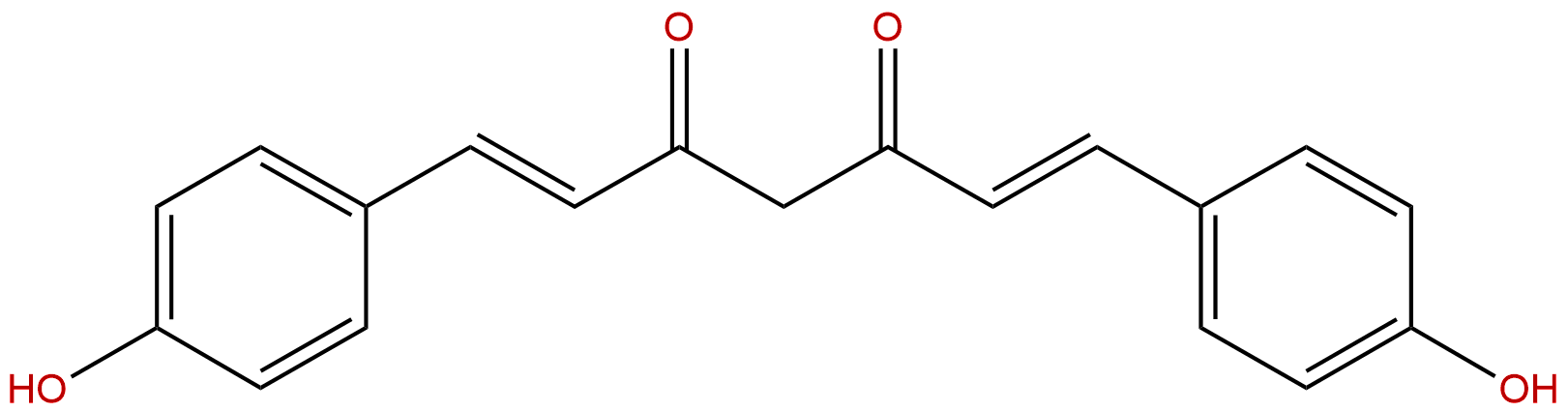
| Formula: | C19H16O4 |
| Mol Weight: | 308.333 |
Product name: Bisdemethoxycurcumin
Synonym name: Curcumin III; Didemethoxycurcumin; Deleted CAS No: 22608-12-4, 85801-92-9, 91884-88-7, 104024-29-5
Catalogue No.: BP0278
Cas No.: 33171-05-0
Formula: C19H16O4
Mol Weight: 308.333
Botanical Source: Curcuma zedoaria , Curcuma longa and Curcuma aromatica. Absent in some Curcuma spp.
Physical Description: Yellow powder
Type of Compound: Phenols
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams, up to kilograms
Inquire for bulk scale.
Descriptions:
Bisdemethoxycurcumin can regulate anti-inflammatory and anti-proliferative responses through a ROS-independent mechanism, also suppresses MCF-7 cells proliferation by inducing ROS accumulation and modulating senescence-related pathways.[1]
Bisdemethoxycurcumin directly accelerates gastric ulcer healing with potency equal to curcumin, its antiulcer effect might be due to its properties of decreasing gastric acid secretion and enhancing the mucosal defensive mechanism through suppression of iNOS-mediated inflammation.[2]
Bisdemethoxycurcumin differentially inhibit cancer cell invasion through the down-regulation of MMPs and uPA.[3]
Bisdemethoxycurcumin induces apoptosis in activated HSCs, but not in hepatocytes, by impairing cellular energetics and causing a downregulation of cytoprotective proteins, likely through a mechanism that involves CBR2.[4]
Bisdemethoxycurcumin has effects on 12-Ο-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-induced tumor promotion.[5]
Bisdemethoxycurcumin has antioxidant activities, inhibits ovarian cancer via reducing oxidative stress mediated MMPs expressions.[6,7]
References:
[1] Sandur SK, Pandey MK, Sung B,et al. Carcinogenesis, 2007, 28(8):1765-73.
[2] Mahattanadul S, Nakamura T, Panichayupakaranant P, et al. Phytomed Int J Phytother Phytopharmacol, 2009, 16(4):342-51.
[3] Li Y B, Gao J L, Zhong Z F, et al. Pharmacol Rep Pr, 2013, 65(3):700-9.
[4]Yodkeeree S, Chaiwangyen W, Garbisa S, et al. J Nutl Biochem, 2009, 20(20):87-95.
[5] Lee P J, Woo S J, Jee J G, et al. Molecules, 2015, 20(1):1277-92.
Jayaprakasha G K, Rao L J, Sakariah K K. Food Chem 2006, 98(4):720-4.
[6]Huang M T, Ma W, Lu Y P, et al. Carcinogenesis, 1995, 16(10):2493-7.
[7] Pei H, Yang Y, Lin C, et al. Sci Rep, 2016, 6,28773.
[8] Jadhav B K, Mahadik K R, Paradkar A R. Chromatographia, 2007, 65(7):483-8.
HPLC of Bisdemethoxycurcumin
