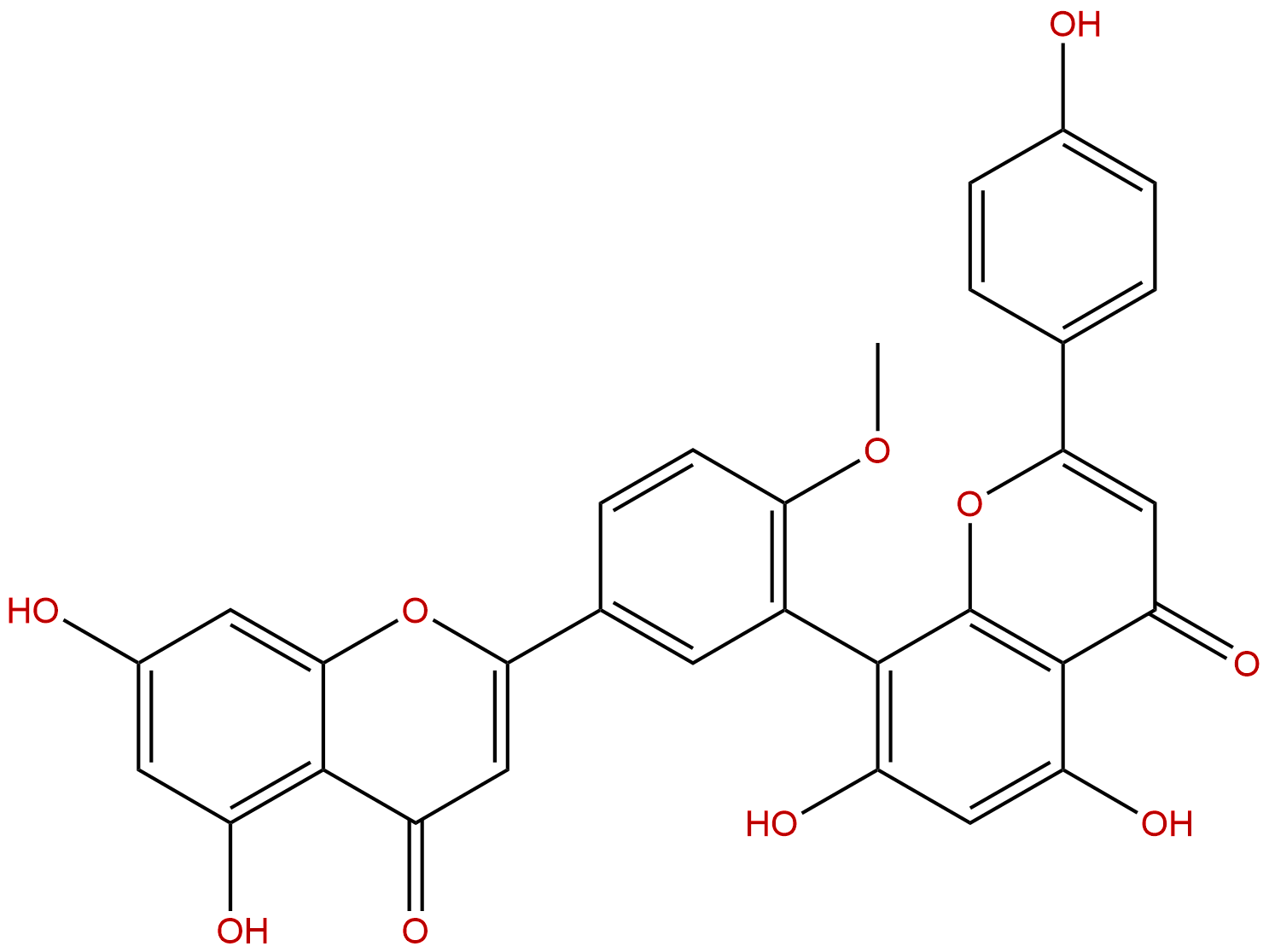
BilobetinCAS No.:521-32-4
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0275 |
| Formula: | C31H20O10 |
| Mol Weight: | 552.491 |
Product name: Bilobetin
Synonym name:
Catalogue No.: BP0275
Cas No.: 521-32-4
Formula: C31H20O10
Mol Weight: 552.491
Botanical Source: Ginkgo biloba L.
Physical Description:
Type of Compound: Flavonoids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams
Inquire for bulk scale.
Description:
Bilobetin treatment ameliorates hyperlipidaemia, lipotoxicity and insulin resistance in rats by stimulating PPARα-mediated lipid catabolism.
References:
Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Apr;165(8):2692-706.
Bilobetin ameliorates insulin resistance by PKA-mediated phosphorylation of PPARα in rats fed a high-fat diet.
The amelioration of insulin resistance by Bilobetin is closely related to its hypolipidaemic effect. The aim of the present study was to determine the insulin-sensitizing mechanism of Bilobetin by elucidating its effect on lipid metabolism.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Rats fed a high-fat diet were treated with Bilobetin for either 4 or 14 days before applying a hyperinsulinaemic-euglycaemic clamp. Triglyceride and fatty acids labelled with radioactive isotopes were used to track the transportation and the fate of lipids in tissues. The activity of lipid metabolism-related enzymes and β-oxidation rate were measured. Western blot was used to investigate the phosphorylation, translocation and expression of PPARα in several tissues and cultured cells. The location of amino acid residues subjected to phosphorylation in PPARα was also studied.Bilobetin ameliorated insulin resistance, increased the hepatic uptake and oxidation of lipids, reduced very-low-density lipoprotein triglyceride secretion and blood triglyceride levels, enhanced the expression and activity of enzymes involved in β-oxidation and attenuated the accumulation of triglycerides and their metabolites in tissues. Bilobetin also increased the phosphorylation, nuclear translocation and activity of PPARα accompanied by elevated cAMP level and PKA activity. Threonine-129-alanine and/or serine-163-alanine mutations on the PPARα genes and PKA inhibitors prevented the effects of Bilobetin on PPARα. However, cells overexpressing PKA appeared to stimulate the phosphorylation, nuclear translocation and activity of PPARα.
CONCLUSIONS:
Bilobetin treatment ameliorates hyperlipidaemia, lipotoxicity and insulin resistance in rats by stimulating PPARα-mediated lipid catabolism. PKA activation is crucial for this process.
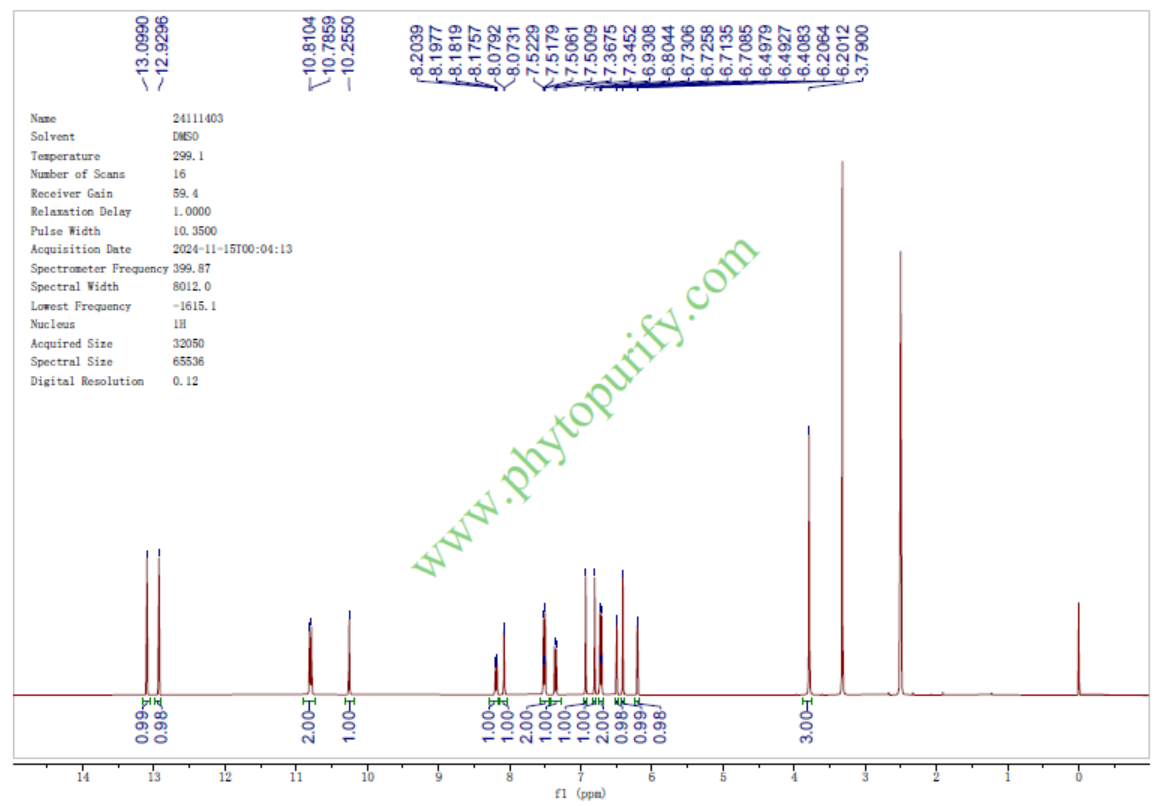
HPLC of Bilobetin

HNMR of Bilobetin