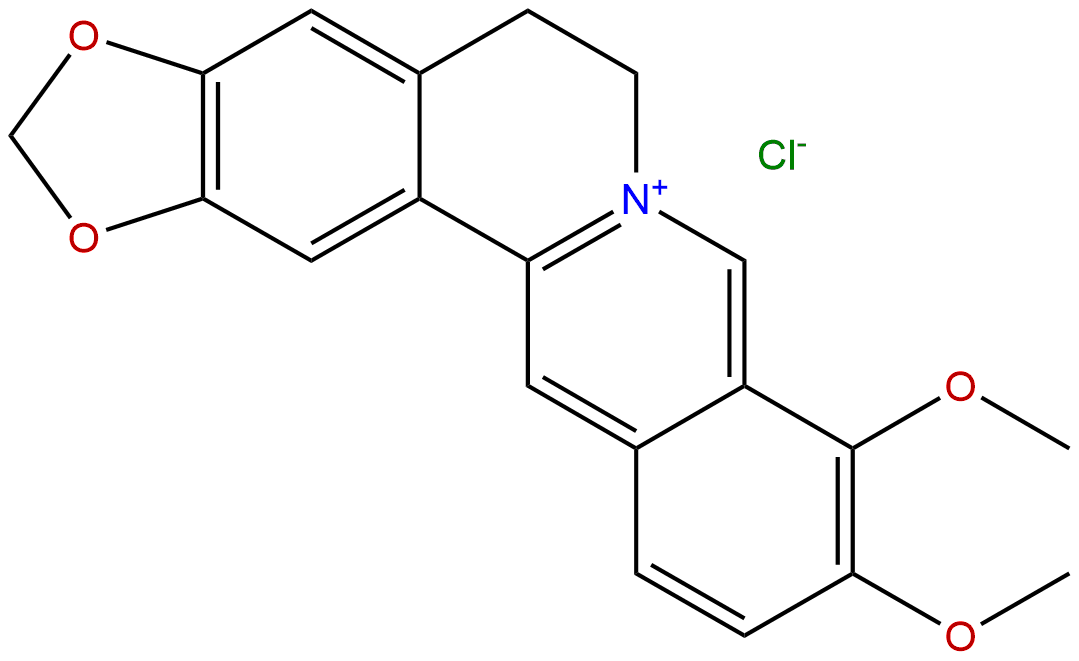
Berberine hydrochlorideCAS No.:633-65-8
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0252 |
| Formula: | C20H18ClNO4 |
| Mol Weight: | 371.817 |
Product name: Berberine hydrochloride
Synonym name: Berberinium chloride
Catalogue No.: BP0252
Cas No.: 633-65-8
Formula: C20H18ClNO4
Mol Weight: 371.817
Botanical Source:
Physical Description: Powder
Type of Compound: Alkaloids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams, up to kilograms
Inquire for bulk scale.
Descriptions:
Berberine hydrochloride (berberine), a natural plant alkaloid derived from Chinese herbal medicine, is characterized by diverse pharmacological effects, such as anticancer and lower elevated blood glucose, it can prevent adhesion by downregulating ICAM-1 and reduce inflammation by inhibiting the TAK1/JNK and TAK1/NF-κB signaling after abdominal surgery, which brings out a good therapeutic approach for the development of clinical application for postoperative abdominal adhesion and inflammation.[1]
Berberine hydrochloride is a conventional component in Chinese medicine, and is characterized by a diversity of pharmacological effects, has anticancer activity and
the chance of regulating glucose and lipid metabolism in cancer cells showing more potential than ever. [2]
Berberine hydrochloride is an alkaloid with little or no fluorescence in water,in sodium dodecylsulfate solutions, the fluorescence intensity of this compound is enhanced several folds by ion-pairing with the anion of the surfactant. [3]
Berberine hydrochloride can significantly attenuate neutrophil infiltration, suppress myeloperoxidase activity, decrease NO, TNF-αand IL-1βproduction, inhibits the phosphorylation of the NF-κB p65 subunit and the degradation of its inhibitor, IκBα, thus, exerts potent anti-inflammatory effects on LPS-induced mouse endometritis and may be a potential therapeutic agent for endometritis.[4]
Berberine hydrochloride has significant reductive ability and radicals scavenging effects, especially on ABTS, hydroxyl radicals and DPPH radicals.[5]
Sensory evaluation of the taste of berberine hydrochloride could be used an Electronic Tongue.[6]
Berberine hydrochloride has antifungi activity.[7]
References:
[1] Zhang Y, Li X, Zhang Q, et al. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 2014, 349(3):417-26.
[2] Wen T, Li Y, Chen M, et al. Int J Nanomed, 2011, 6(default):1773-7.
[3] Iwunze M O. Monatshefte Fuer Chemie/chemical Monthly, 2000, 131(5):429-35.
[4] Fu K, Lv X, Li W, et al. Int Immunopharmacol, 2014, 24(1):128-32.
[5] Luo A, Fan Y, Luo A, et al. J Med Plant Res, 2011, 5(16):3702-7.
[6] Wang Y, Feng Y, Wu Y, et al. Fitoterapia, 2013, 86(4):137-43.
[7] Nakamoto K, Sadamori S, Hamada T. J Prosthet Dent, 1990, 64(6):691-4.
[8] Xiang L I, Liu G Y, Jian-Li M A, et al. Pharmaceutical Journal of Chinese Peoples Liberation Army, 2013(05):458-60.
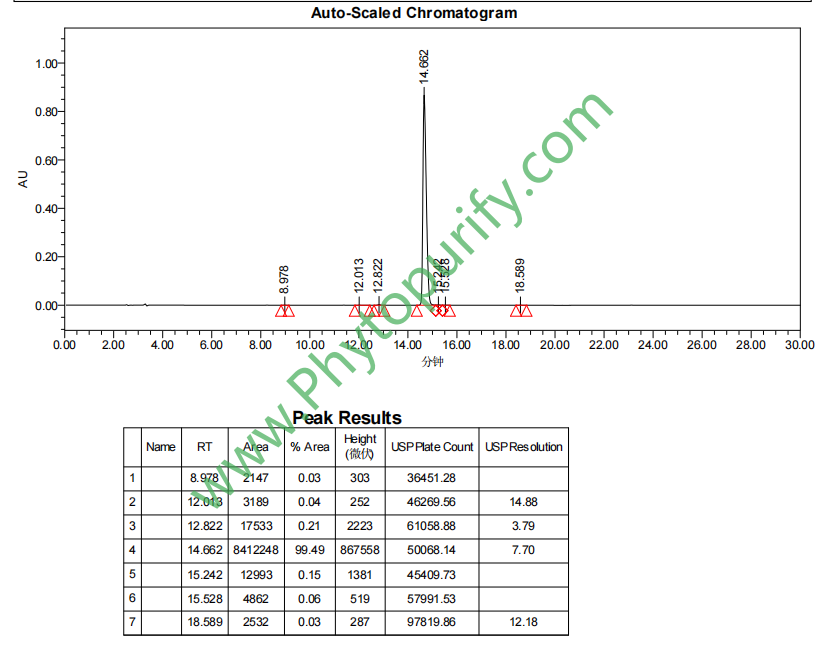
HPLC of Berberine hydrochloride