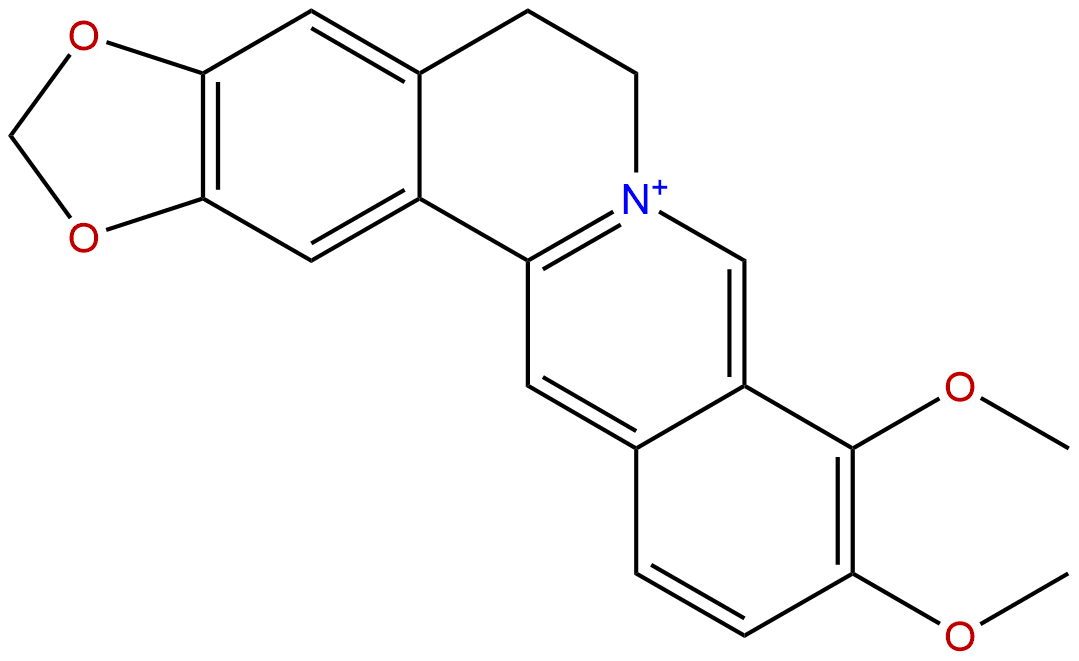
BerberineCAS No.:2086-83-1
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0251 |
| Formula: | C20H18NO4+ |
| Mol Weight: | 336.366 |
Product name: Berberine
Synonym name: Berbericine
Catalogue No.: BP0251
Cas No.: 2086-83-1
Formula: C20H18NO4+
Mol Weight: 336.366
Botanical Source: Quaternary alkaloid from many Berberis and Mahonia spp. (Berberidaceae) and very many other spp. in several different families
Physical Description: Yellow powder
Type of Compound: Alkaloids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams, up to kilograms
Inquire for bulk scale.
Descriptions:
Berberine, a naturally occurring isoquinoline alkaloid, has been shown to possess anti-inflammatory and antitumor properties in some in vitro systems; berberine-induced apoptosis of human prostate cancer cells is mediated primarily through the caspase-dependent pathway, the effectiveness of berberine in checking the growth of androgen-insensitive, as well as androgen-sensitive, prostate cancer cells without affecting the growth of normal prostate epithelial cells indicates that it may be a promising candidate for prostate cancer therapy.[1]
Berberine has beneficial effects in the treatment of diabetes and obesity at least in part via stimulation of AMPK activity, can reduce body weight and cause a significant improvement in glucose tolerance without altering food intake in mice, downregulate the expression of genes involved in lipogenesis and upregulate those involved in energy expenditure in adipose tissue and muscle, and activate AMP-activated protein kinase.[2]
Berberine can ameliorate β-amyloid pathology, gliosis, and cognitive impairment in an Alzheimer's disease transgenic mouse model.[3]
Berberine can suppress inflammatory agents-induced cytokine production in lung cells, the suppression of berberine on the cytokine production resulted from the inhibition of inhibitory κB-α phosphorylation and degradation, suggests the potential role of berberine in the treatment of pulmonary inflammation.[4]
Berberine down-regulates u-PA, MMP-2 and -9 expressions in SCC-4 cells through the FAK, IKK and NF-kappaB mediated pathways and a novel function of berberine is to inhibit the invasive capacity of malignant cells.[5]
Berberine has anti- proliferation activity against human esophageal cancer cell lines.[6]
References:
[1] Mantena S K, Sharma S D, Katiyar S K. Mol Cancer Ther, 2006, 5(2):296-308.
[2] Yun S L, Kim W S, Kang H K, et al. Diabetes, 2006, 55(8):2256-64.
[3] Durairajan S, Liu L F, Lu J H, et al. Neurobiol Aging, 2012, 33(12):2903-19.
[4] Lee C H, Chen J C, Hsiang C Y, et al. Pharmacol Res, 2007, 56(3):193-201.
[5] Ho Y T, Yang J S, Li T C, et al. Cancer Lett, 2009, 279(2):155-62.
[6] Iizuka N, Miyamoto K, Okita K, et al. Cancer Lett, 2000, 148(1):19-25.
[7] Jun-Lin H U, Tan J L, Fei Y Q, et al. Chinese J Hospital Pharma, 2014, 34(1):50-2.
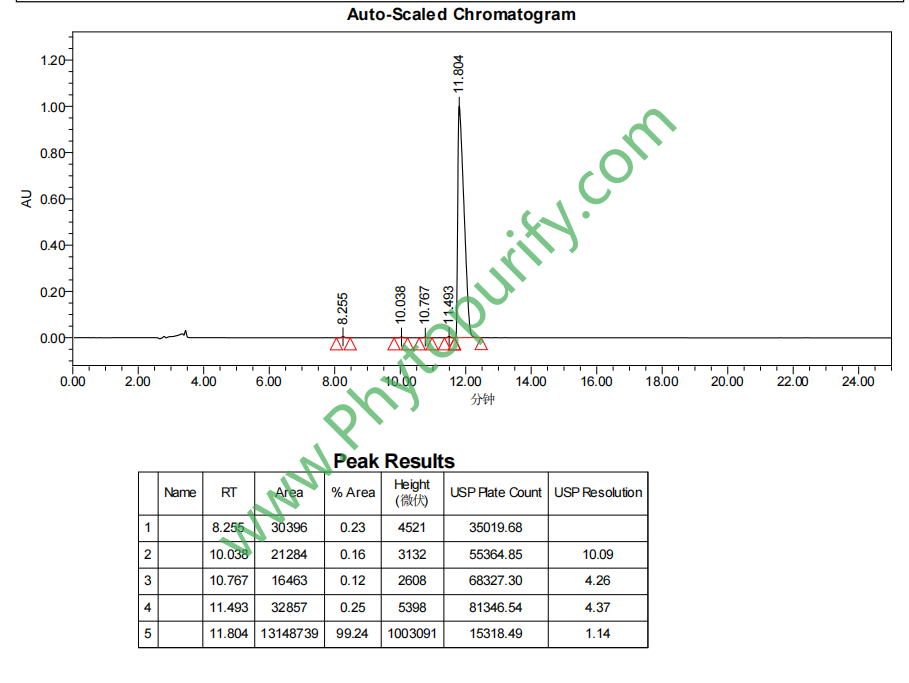
HPLC of Berberine