BaicaleinCAS No.:491-67-8
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0232 |
| Formula: | C15H10O5 |
| Mol Weight: | 270.24 |
Product name: Baicalein
Synonym name: 5,6,7-Trihydroxyflavone; Noroxylin
Catalogue No.: BP0232
Cas No.: 491-67-8
Formula: C15H10O5
Mol Weight: 270.24
Botanical Source: Scutellaria spp. and other plants
Physical Description: Yellow powder
Type of Compound: Flavonoids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams, up to kilograms
Inquire for bulk scale.
Descriptions:
Baicalin, saikosaponins, and baicalein have antitumor effects on human hepatoma cell lines and bladder cancer cell lines.[1,2]
Baicalin, wogonin,and baicalein inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 gene expressions induced by nitric oxide synthase inhibitors and lipopolysaccharide .[3]
Baicalin and its aglycone baicalein have widely investigated in hematological malignancies because both of them exhibit remarkable pharmacological properties.[4]
Baicalin, baicalein, and wogonin have antioxidant and free radical scavenging effects.[5]
Baicalin exhibits the greatest inhibition activity against carrageenan-induced rat paw edema.[6]
Baicalein can induce cancer cell death and proliferation retardation by the inhibition of CDC2 kinase and survivin associated with opposite role of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and AKT.[7]
References:
[1] Motoo Y, Sawabu N. Cancer Lett, 1994, 86(1):91-5.
[2] Ikemoto S, Sugimura K, Yoshida N, et al. Urology, 2000, 55(6):951-5.
[3] Chen Y C, Shen S C, Chen L G, et al. Biochem Pharmacol, 2001, 61(11):1417-27.
[4] Chen H, Gao Y, Wu J, et al. Cancer Lett, 2014, 354(1):5-11.
[5] Shieh D E, Liu L T, Lin C C. Anticancer Res, 2000, 20(5A):2861-5.
[6] ChunChing Lin, DenEn Shieh. Am J Chinese Med, 1996, 24(1):31-6.
[7] Chao J, Su W H. Mol Cancer Ther, 2007, 6(11):3039-48.
[8] Dong W J, Liu Y L. Chinese J Pharma Anal, 2009, 29(3):2120-2.
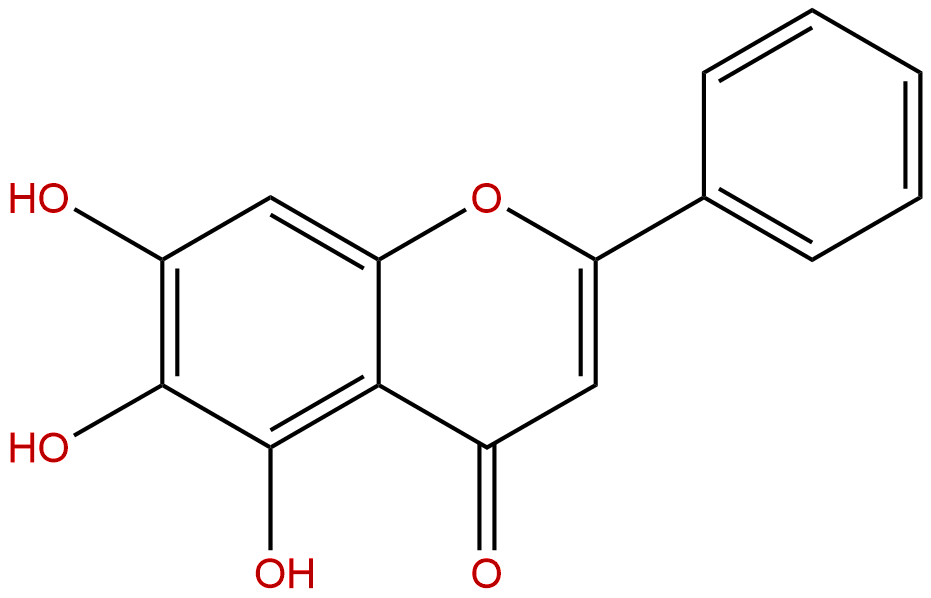
NMR of Baicalein
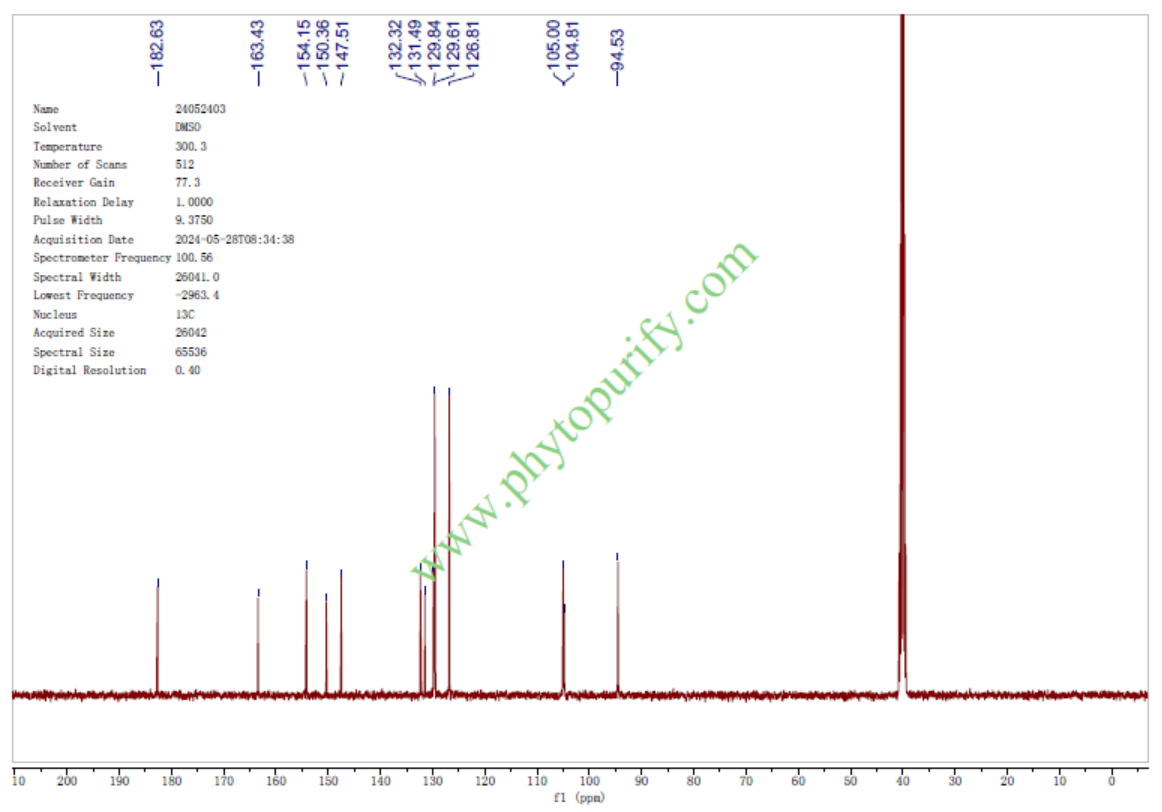
HPLC of Baicalein