
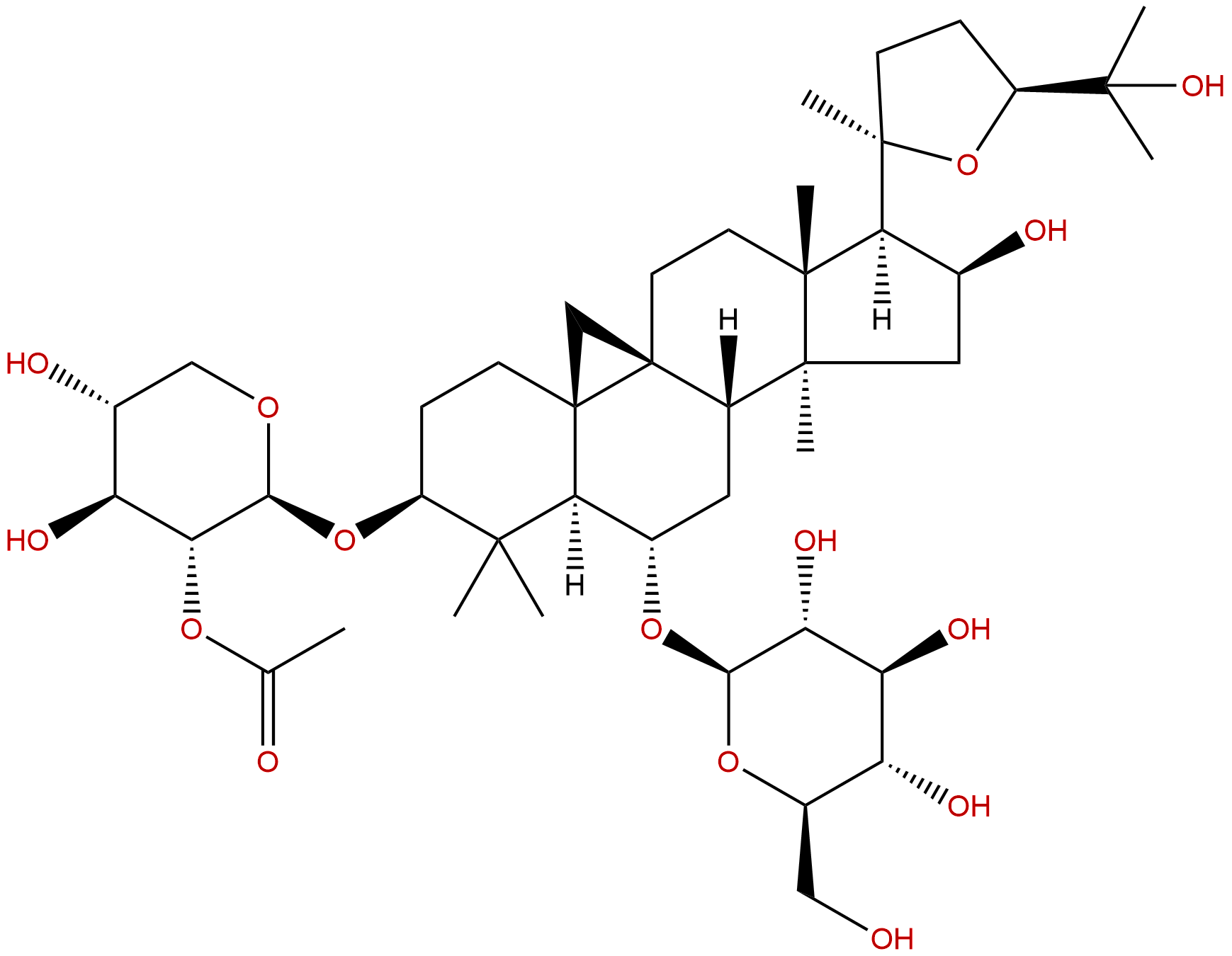
Astragaloside IICAS No.:84676-89-1
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0211 |
| Formula: | C43H70O15 |
| Mol Weight: | 827.018 |
Product name: Astragaloside II
Synonym name: Astrasieversianin VIII; Cyclosieversioside D; Cyclosiversioside D
Catalogue No.: BP0211
Cas No.: 84676-89-1
Formula: C43H70O15
Mol Weight: 827.018
Botanical Source: From Astragalus membranaceus, Astragalus sieversianus, Astragalus basineri, Astragalus spinosus and Astragalus trigonus
Physical Description: Powder
Type of Compound: Triterpenoids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams, up to kilograms
Inquire for bulk scale.
Descriptions:
Astragaloside II can downregulate the expression of the P-gp and mdr1 gene, suppress phosphorylation of extracellular signal regulated kinase 1/2, p38 and c-Jun N-terminal kinase, suggests that Astragaloside II is a potent multidrug resistance (MDR) reversal agent and may be a potential adjunctive agent for hepatic cancer chemotherapy.[1]
Astragaloside II induces osteogenic activities of osteoblasts through the bone morphogenetic protein-2/MAPK and Smad1/5/8 pathways, it may become a novel candidate that is beneficial for stimulating the osteoblastic activity resulting in bone formation.[2]
Astragaloside II has immunomodulating activity, can trigger T cell activation through regulation of CD45 protein tyrosine phosphatase activity.[3]
Astragaloside II in conjunction with cisplatin can significant reduce cell viability, and arrest in S phase and increased apoptosis, suggests that astragaloside II can be served as autophagy inhibitor which restores chemosensitivity of anticancer agent cisplatin and enhances tumor cell death.[4]
References:
[1] Huang C, Xu D, Xia Q, et al. J Pharm Pharmacol, 2012, 64(12):1741-50.
[2] Kong X H, Niu Y B, Song X M, et al. Int J Mol Med 2012, 29(6):1090-8.
[3] Chun-ping, Li-xin, Li-fei, et al. Acta Pharm Sin, 2013, 34(4):522-30.
[4] Yang C, Wu C, Xu D, et al. Biomed Pharmacother, 2016, 81:166-75.
[5] Zhao J, Yan W, Dai G. Chromatographia, 2005, 62(9-10):543-6.
HPLC of Astragaloside II
