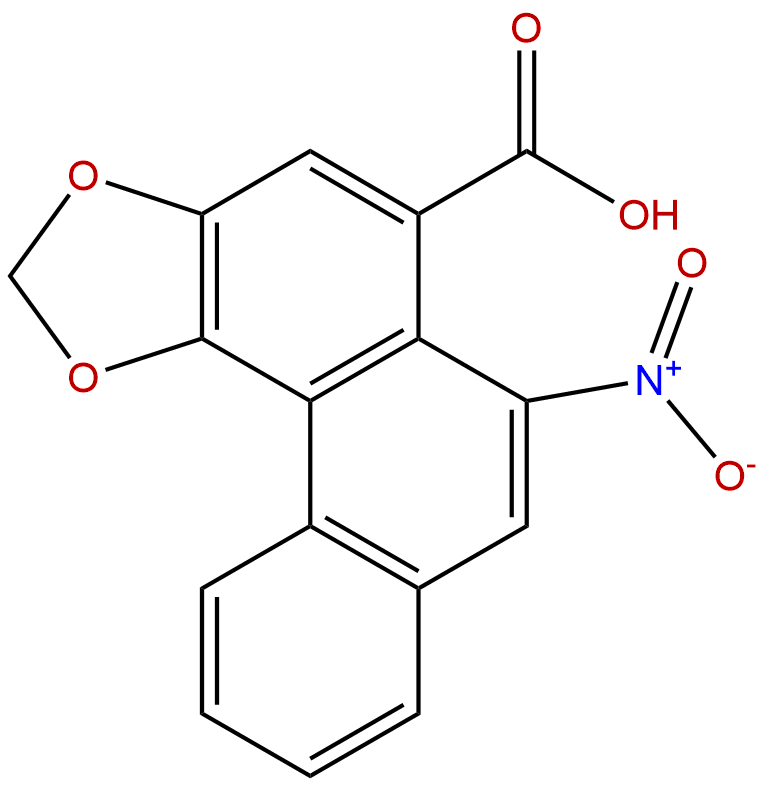
Aristolochic Acid BCAS No.:475-80-9
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0193 |
| Formula: | C16H9NO6 |
| Mol Weight: | 311.249 |
Product name: Aristolochic Acid B
Synonym name: Aristolochic Acid II
Catalogue No.: BP0193
Cas No.: 475-80-9
Formula: C16H9NO6
Mol Weight: 311.249
Botanical Source: Alkaloid from Aristolochia argentina, Aristolochia clematitis, Aristolochia esperanzae, Aristolochia longa, Aristolochia manshuriensis, Aristolochia rotunda, Aristolochia pallida, Aristolochia sipho (Aristolochia durior) and from the Chinese drugs Ching-
Physical Description: Yellow powder
Type of Compound: Miscellaneous
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams, up to kilograms
Inquire for bulk scale.
Descriptions:
Aristolochic acid II (AAII), one of the major components of the carcinogenic plant extract aristolochic acid, is known to be mutagenic and to form DNA adducts in vitro and in vivo,
AAII shows more carcinogenic risk than aristolochic acid I, and this may be, at least partly, the result of its increased levels in kidney and plasma.[1,2]
Aristolochic acid exhibit significant toxicity, and the short-term toxicity of aristolochic acid-II and aristolochic acid is similar to each other, renal but not hepatic failure induced by aristolochic acid could be prevented by pentoxifylline.[3]
References:
[1] Pfau W, Schmeiser H H, Wiessler M. Cheml Res Toxicol, 1991, 4(5):581-6.
[2] Xing G, Qi X, Min C, et al. Mutat Res-Fund Mol M, 2012, 743(1-2):52-8.
[3] Yeh Y H, Lee Y T, Hsieh H S, et al. Food Chem Toxicol , 2008, 46(3):1157-63.
[4] Zhu G, Wang Z, Wang Q, et al. China Pharmacy, 2006, 17(18):21-4.
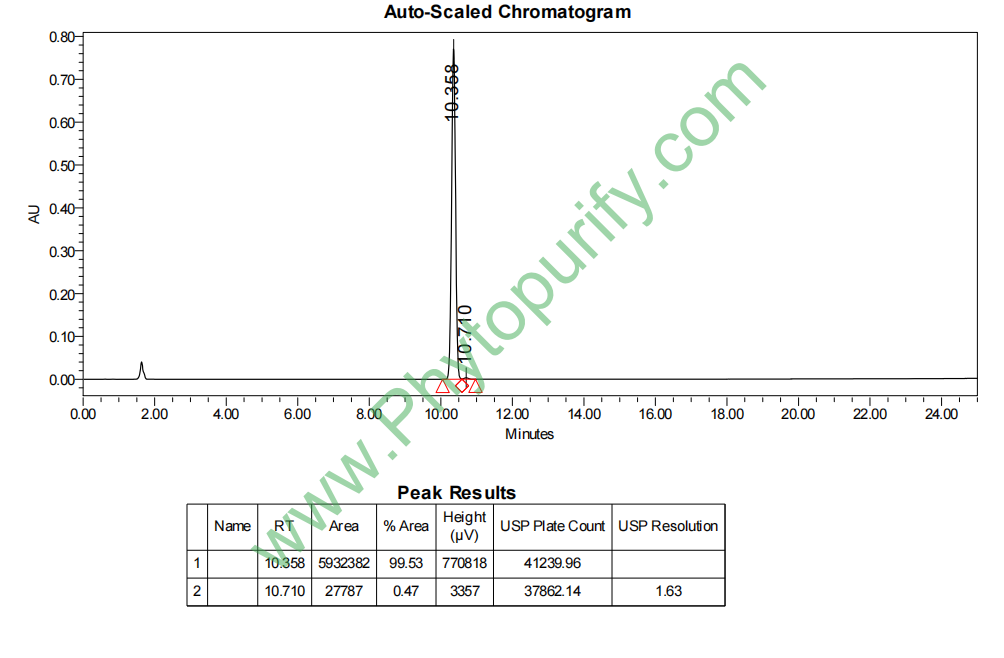
HPLC of Aristolochic Acid B