
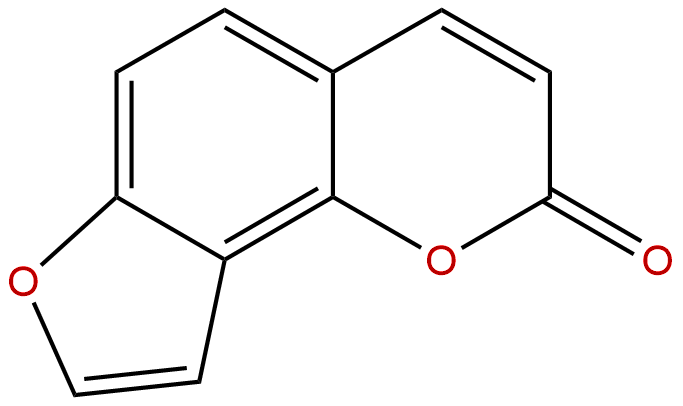
AngelicinCAS No.:523-50-2
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0171 |
| Formula: | C11H6O3 |
| Mol Weight: | 186.166 |
Product name: Angelicin
Synonym name: Isopsoralen; Bakuchicin
Catalogue No.: BP0171
Cas No.: 523-50-2
Formula: C11H6O3
Mol Weight: 186.166
Botanical Source: roots and leaves of angelica (Angelica archangelica). Found in roots and on surface of parsnips and diseased celery. Also in other Angelica spp, Heracleum spp. and others
Physical Description: Powder
Type of Compound: Coumarins
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams, up to kilograms
Inquire for bulk scale.
Descriptions:
Angelicin is a furocoumarin found in Psoralea corylifolia L. fruit, can block the phosphorylation of IκBα, NFκBp65, p38 MAPK, and JNK in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury model, suggests that angelicin was potentially advantageous to prevent inflammatory diseases by inhibiting NF-κB and MAPK pathways, it might be a potential new agent for prevention of inflammatory reactions and diseases in the clinic.[1]
Angelicin, compared with cytosine arabinoside, mithramycin and cisplatin, is a powerful inducer of erythroid differentiation and -globin mRNA accumulation of human leukemia K562 cells, it is a potential therapeutic approach in hematological disorders, including -beta-thalassemia and sickle cell anemia.[2]
A novel angelicin derivative 6a was identified to inhibit influenza A (H1N1) virus induced Cytopathic effect in Madin-Darby canine kidney cell culture in low micromolar range, these compounds act as anti-influenza agents by inhibiting ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex associated activity and have the potential to be developed further, which could form the basis for developing additional defense against influenza pandemics.[3]
Angelicin is structurally related to psoralens, a well-known chemical class of photosensitizers used for its antiproliferative activity in treatment of different skin disease, angelicin is an effective apoptosis-inducing natural compound of human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells which suggests that this compound may have a role in future therapies for human neuroblastoma cancer.[4]
References:
[1] Liu F, Sun G Q, Gao H Y, et al. J Surg Res, 2013, 185(1):300-9.
[2] Lampronti I, Bianchi N M, Fibach E, et al. Eur J Haematol, 2003, 71(3):189-95.
[3] Yeh J, Coumar M, Horng J, et al. J Med Chem, 2010, 53(4):1519-33.
[4] Rahman M A, Kim N H, Yang H, et al. Mol Cell Biochem, 2012, 369(1-2):95-104.
[5] Yan R, Liu Z, Luo J. Chinese Medicine Modern Distance Education of China, 2008,6(11):1329-30.
HPLC of Angelicin
