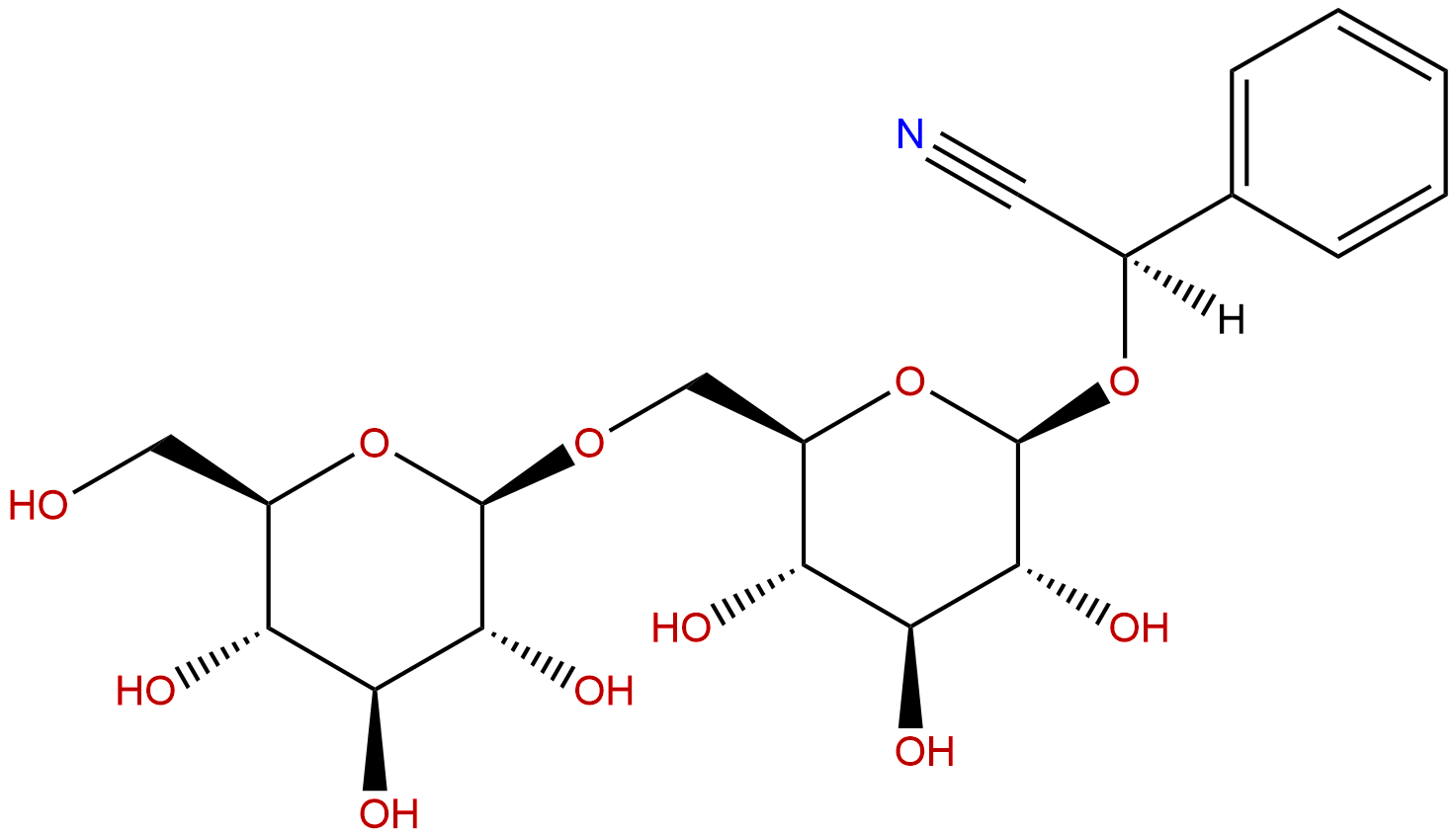
AmygdalinCAS No.:29883-15-6
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0162 |
| Formula: | C20H27NO11 |
| Mol Weight: | 457.432 |
Product name: Amygdalin
Synonym name: Amygdaloside; Mandelonitrile gentiobioside; Glucoprunasin; Laetrile; Vitamin B17
Catalogue No.: BP0162
Cas No.: 29883-15-6
Formula: C20H27NO11
Mol Weight: 457.432
Botanical Source: Bitter glycoside of the Rosaceae, found esp. in kernels of cherries, peaches and apricots. Present in cold pressed bitter almond oil from the above sources prior to enzymic hydrolysis and steam distillation for food use
Physical Description: Powder
Type of Compound: Phenols
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams, up to kilograms
Inquire for bulk scale.
Descriptions:
Amygdalin induces apoptotic cell death in human DU145 and LNCaP prostate cancer cells by caspase-3 activation through down-regulation of Bcl-2 and up-regulation of Bax,suggests it may offer a valuable option for the treatment of prostate cancers.[1]
Amygdalin suppresses the prostaglandin E(2) synthesis and the nitric oxide production by inhibiting the LPS-stimulated mRNA expressions of COX-2 and iNOS in the mouse BV2 cells.[2]
Amygdalin can inhibit genes related to cell cycle in SNU-C4 human colon cancer cells.[3]
References:
[1] Chang H K, Shin M S, Yang H Y, et al. Biol Pharm Bull, 2006, 29(8):1597-602.
[2] Yang H Y, Chang H K, Lee J W, et al. Neurol Res, 2013, 29 suppl 1(1):59-64(6).
[3] Park H J, Yoon S H, Han L S, et al. World J Gastroentero, 2005, 11(33):5156-61.
[4] Zhou C, Chen K, Sun C, et al. Biomed Chromatogr, 2007, 21(7):755-61.
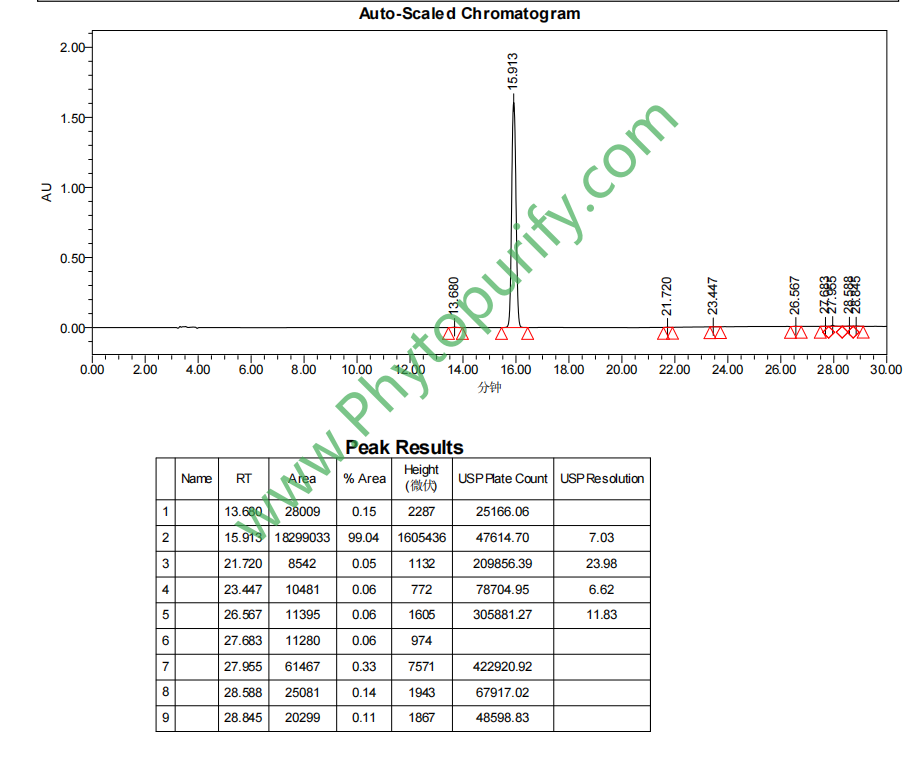
HPLC of Amygdalin