
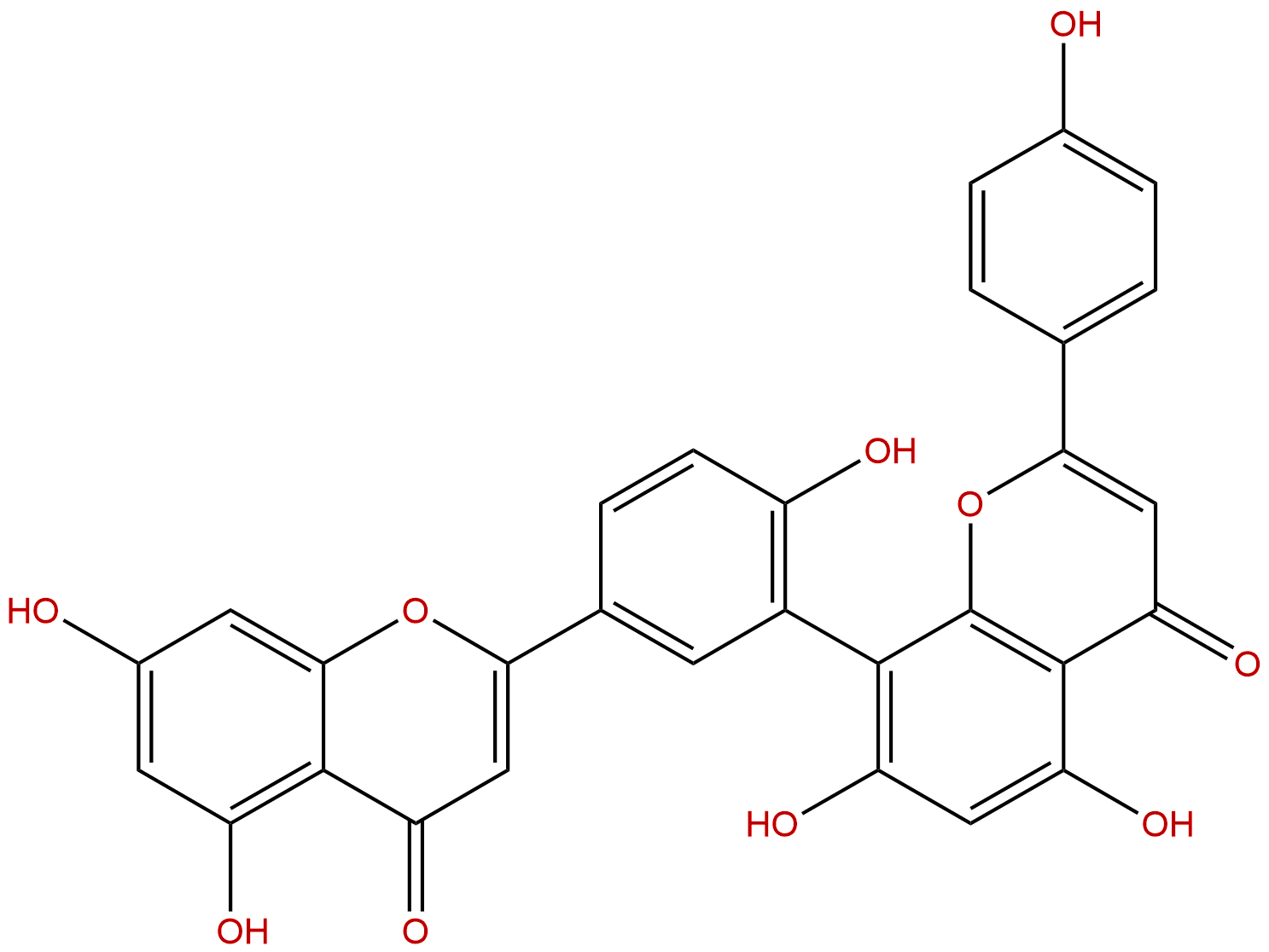
AmentoflavoneCAS No.:1617-53-4
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0161 |
| Formula: | C30H18O10 |
| Mol Weight: | 538.464 |
Product name: Amentoflavone
Synonym name:
Catalogue No.: BP0161
Cas No.: 1617-53-4
Formula: C30H18O10
Mol Weight: 538.464
Botanical Source: Metasequoia glyptostroboides, Viburnum prunifolium, Podocarpus gracilior, Garcinia livingstonei, Selaginella willdenowii, Rhus succedanea, Garcinia multiflora, Ginkgo biloba, Cupressocyparis leylandii, Cryptomeria japonica, Amentotaxus formos
Physical Description: Yellow powder
Type of Compound: Flavonoids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams, up to kilograms
Inquire for bulk scale.
Descriptions:
Amentoflavone, a biflavonoid with antiinflammatory activity, inhibits NF-κB/DNA binding activity potently along with inhibition of degradation of IκBα and NF-κB translocation into nucleus in TNFα-activated A549 cells.[1]
Amentoflavone has the inhibition of LPS-induced NO formation, is due to its inhibition of NF-kappaB by blocking degradation, which may be the mechanistic basis of the anti-inflammatory effects of amentoflavone.[2]
Amentoflavone has been shown to inhibit tumor metastasis in vivo, amentoflavone treatment reduces experimental tumor metastasis and suggest that such an action is associated with attenuation of tumor invasion, proliferation and angiogenesis.[3]
Amentoflavone has been shown to inhibit tumor metastasis in vivo, inhibits experimental tumor metastasis through a regulatory mechanism involving MMP-2, MMP-9, prolyl hydroxylase, lysyl oxidase, VEGF, ERK-1, ERK-2, STAT-1, NM23 and cytokines in lung tissues of C57BL/6 mice.[4]
Amentoflavone and its derivatives as novel natural inhibitors of human Cathepsin B(CatB), CatB is a member of the papain superfamily of cysteine proteases and has been implicated in the pathology of numerous diseases, including arthritis and cancer. [5]
Amentoflavone induces breast cancer apoptosis through blockade of fatty acid synthesis.[6]
Amentoflavone exhibits potent antifungal activity against several pathogenic fungal strains but has a very low hemolytic effect on human erythrocytes, it induces the accumulation of intracellular trehalose on C. albicans as a stress response to the drug, and disrupts the dimorphic transition that forms pseudo-hyphae during pathogenesis, it has great potential to be a lead compound for the development of antifungal agents.[7]
References:
[1] Banerjee T, Valacchi G, Ziboh V A, et al. Mol Cell Biochem, 2002, 238(1-2):105-10.
[2] Woo E R, Lee J Y, Cho I J, et al. Pharmacol Res, 2005, 51(6):539-46.
[3] Guruvayoorappan C, Kuttan G. Biochemistry, 2008, 73(2):209-18.
[4] Guruvayoorappan C, Kuttan G. Immunopharm Immunot, 2008, 30(4):711-27.
[5] Pan X, Tan N, Zeng G, et al. Bioorg Med Chem, 2005, 13(20):5819-25.
[6] Lee J, Lee M, Oh W, et al. Biol Pharm Bull, 2009, 32(8):1427-32.
[7] Jung H J, Sung W S, Yeo S H, et al. Arch Pharm Res, 2006, 29(9):746-51.
[8] Sun D M, Luo W H, Zhi-Yong L I. Journal of Chinese medicinal materials, 2006, 29(29):26-8.
HPLC of Amentoflavone
