
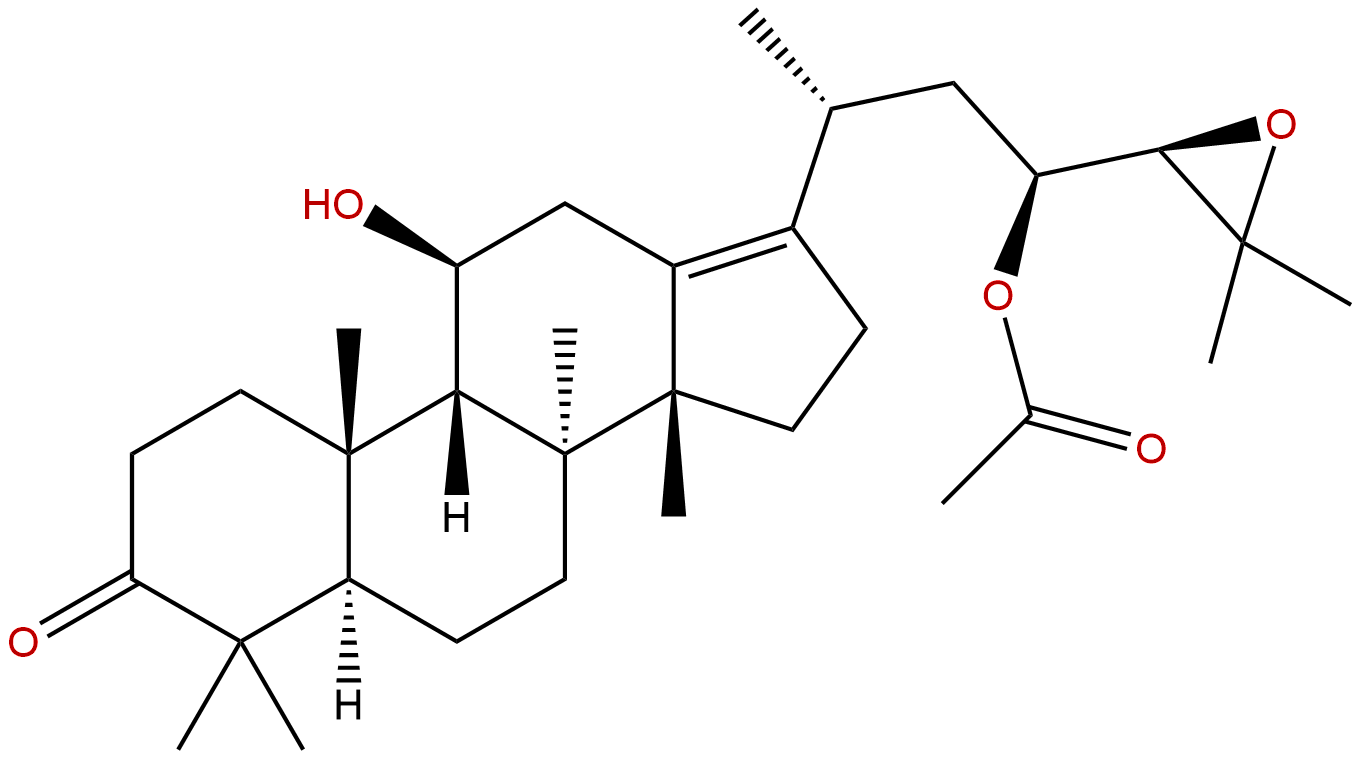
Alisol B AcetateCAS No.:26575-95-1
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0136 |
| Formula: | C32H50O5 |
| Mol Weight: | 514.747 |
Synonym name: 23-O-Acetylalisol B; Alisol B,23-acetate
Catalogue No.: BP0136
Cas No.: 26575-95-1
Formula: C32H50O5
Mol Weight: 514.747
Botanical Source: Alisma plantago-aquatica
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Can be supplied from milligrams to grams.
For Reference Standard and R&D, Not for Human Use Directly.
Inquire for bulk scale.
Description:
Alisol B 23-acetate, a partial non-competitive inhibitor of P-gp, it may be a potential MDR reversal agent. Alisol B 23-acetate produces protective effects against ANIT-induced hepatotoxity and cholestasis, due to FXR-mediated gene regulation; it obviously inhibits proliferation of the three ovarian cancer cell lines, possesses anti-proliferation, anti-migration and anti-invasion activities as a single agent on ovarian cancer cells.
References:
Biochem Pharmacol. 2004 Sep 1;68(5):843-55.
Reversal of P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance by Alisol B 23-acetate.
Herbal drugs were screened for their activity in reversing multidrug resistance (MDR) in P-glycoprotein (P-gp) over-expressing cancer cells.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Through bio-assay guided fractionation an active compound was isolated from Rhizoma Alismatis, the underground part of Alisma orientale and the chemical structure of the isolate compound was confirmed by HPLC, LC-MS and NMR as Alisol B 23-acetate (ABA). ABA restored the sensitivity of MDR cell lines HepG2-DR and K562-DR to anti-tumor agents that have different modes of action but are all P-gp substrates. It restored the activity of vinblastine, a P-gp substrate, in causing G2/M arrest in MDR cells. In a dose-dependent manner, ABA increased doxorubicin accumulation and slowed down the efflux of rhodamin-123 from MDR cells. ABA inhibited the photoaffinity labeling of P-gp by [125I]iodoarylazidoprazosin and stimulated the ATPase activity of P-gp in a concentration-dependent manner, suggesting that it could be a transporter substrate for P-gp. In addition, ABA was also a partial non-competitive inhibitor of P-gp when verapamil was used as a substrate.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our results suggest that ABA may be a potential MDR reversal agent and could serve as a lead compound in the development of novel drugs.
Food Funct. 2015 Apr 8;6(4):1241-50.
Protective effects of alisol B 23-acetate from edible botanical Rhizoma alismatis against carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in mice.
Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced hepatotoxicity is a common syndrome with simultaneous severe hepatocyte death and acute cholestasis.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The purpose of the present study is to investigate the hepatoprotective effect of Alisol B 23-acetate (AB23A), a natural triterpenoid from edible botanical Rhizoma alismatis, on acute hepatotoxicity induced by CCl4 in mice, and further to elucidate the involvement of farnesoid X receptor (FXR), signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 (STAT3) in the hepatoprotective effect. H&E staining, BrdU immunohistochemistry and TUNEL assay were used to identify the amelioration of histopathological changes, hepatocyte proliferation and apoptosis. Real-time PCR and western blot assay were used to elucidate the mechanisms underlying Alisol B 23-acetate hepatoprotection. The results indicated that Alisol B 23-acetate treatment in a dose-dependent manner resulted in protection against hepatotoxicity induced by CCl4via FXR activation. Through FXR activation, Alisol B 23-acetate promoted hepatocyte proliferation via an induction in hepatic levels of FoxM1b, Cyclin D1 and Cyclin B1. Alisol B 23-acetate also reduced hepatic bile acids through a decrease in hepatic uptake transporter Ntcp, bile acid synthetic enzymes Cyp7a1, Cyp8b1, and an increase in efflux transporter Bsep, Mrp2 expression. In addition, Alisol B 23-acetate induced the expression of STAT3 phosphorylation, and STAT3 target genes Bcl-xl and SOCS3, resulting in decreased hepatocyte apoptosis.
CONCLUSIONS:
In conclusion, Alisol B 23-acetate produces a protective effect against CCl4-induced hepatotoxicity, due to FXR and STAT3-mediated gene regulation.
HPLC of 23-O-Acetylalisol B
