
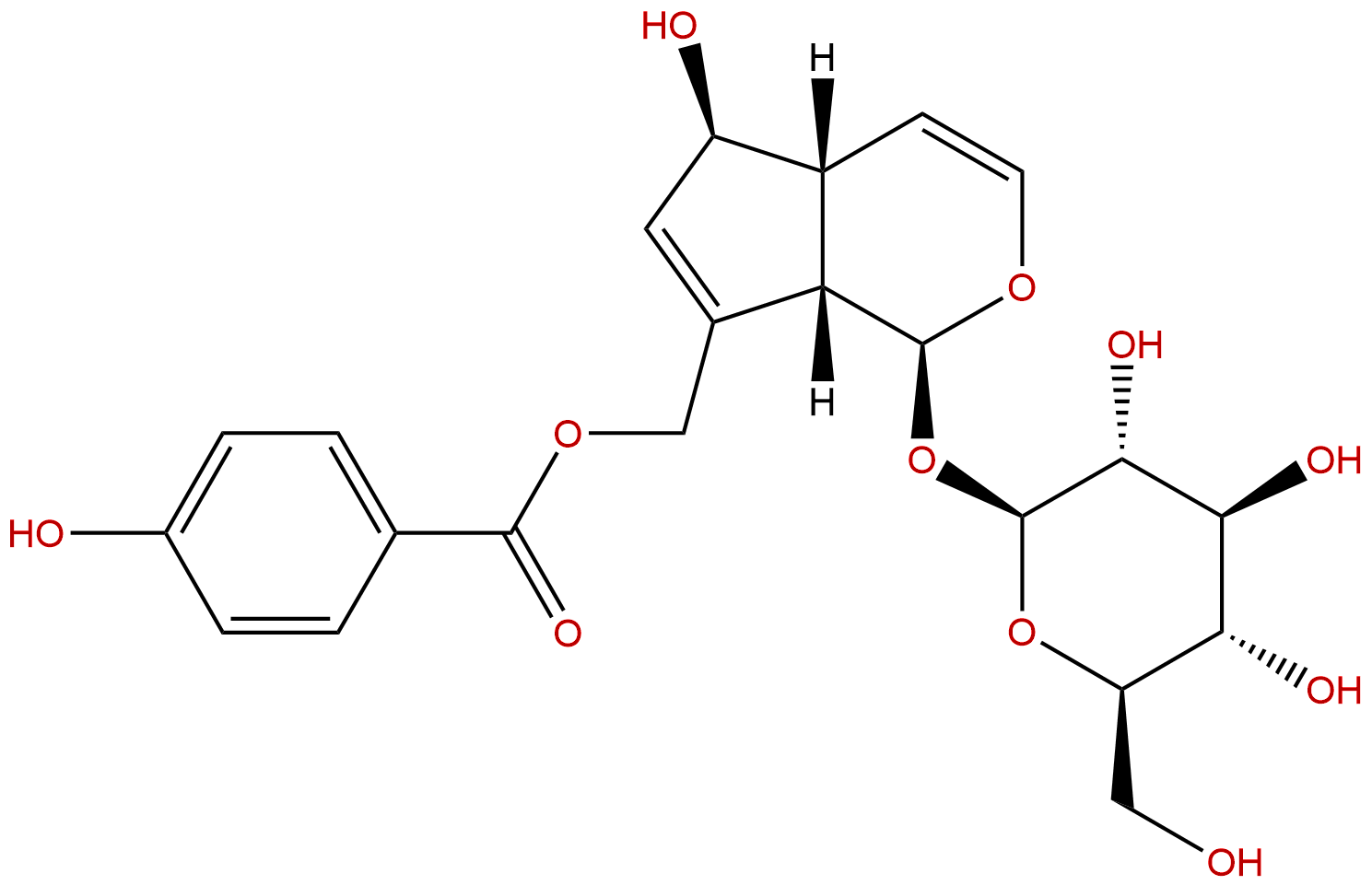
AgnusideCAS No.:11027-63-7
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0125 |
| Formula: | C22H26O11 |
| Mol Weight: | 466.439 |
Product name: Agnuside
Synonym name: Agnoside; Buddlejoside A
Catalogue No.: BP0125
Cas No.: 11027-63-7
Formula: C22H26O11
Mol Weight: 466.439
Botanical Source: Yitex negundo fructus
Physical Description:
Type of Compound: Iridoids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams
Inquire for bulk scale.
Description:
Agnuside has anti-arthritic activity, it also shows inhibition of vascular permeability and leukocyte migration in vivo.It inhibited an array of pro-inflammatory mediators (PGE(2) and LTB(4)) and T-cell-mediated cytokines (IL-2, TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-4, IL-10, IL-17).
References:
Inflamm Res. 2012 Apr;61(4):293-304.
Anti-arthritic activity of agnuside mediated through the down-regulation of inflammatory mediators and cytokines.
The purpose of this study was to elucidate the probable mechanism for the anti-arthritic activity of Agnuside (AGN), a compound isolated from the leaf extract of Vitex negundo.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The anti-inflammatory activity of AGN within a dose range of 1.56-12.50 mg/kg in normal and adrenalectomized rats was evaluated against different inflammagens. An array of pro-inflammatory mediators (PGE(2) and LTB(4)) and T-cell-mediated cytokines (IL-2, TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-4, IL-10, IL-17) was assayed using flow cytometry, in arthritic paw tissue homogenate and splenocytes of treated animals. Significant anti-arthritic activity was observed in the polyarthritis test in rats and this was associated with significant suppression of inflammatory mediators and T-cell-mediated cytokines (Th1/Th2). The anti-inflammatory activity in adrenalectomized rats confirmed that the effect of AGN is not mediated by the pituitary-adrenal axis. AGN also showed inhibition of vascular permeability and leukocyte migration in vivo.
CONCLUSIONS:
The study suggests the possible development of AGN as a therapeutic agent in the treatment of arthritis by the modulation of the host immune response.
HPLC of Agnuside
