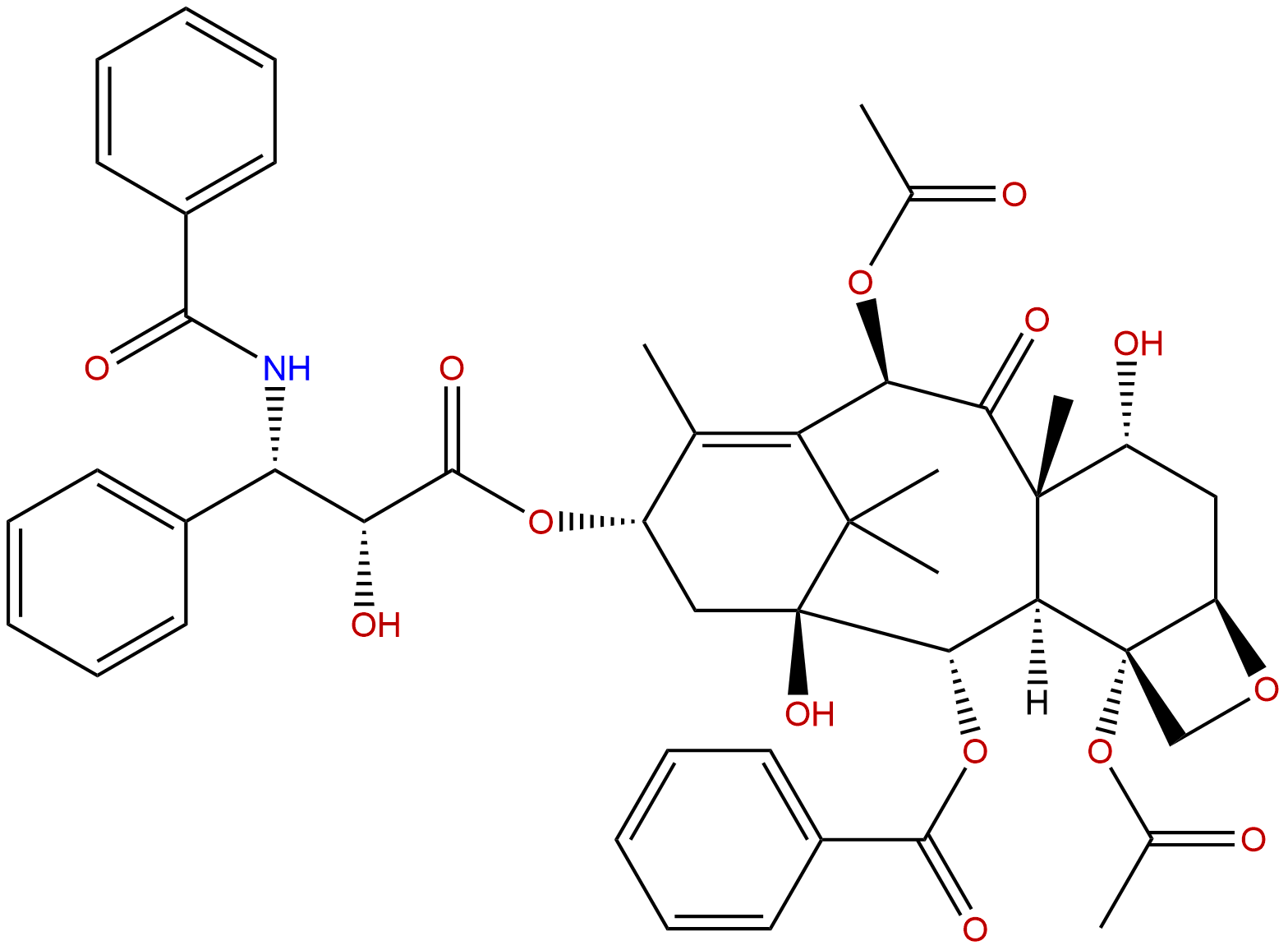
7-EpitaxolCAS No.:105454-04-4
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0098 |
| Formula: | C47H51NO14 |
| Mol Weight: | 853.918 |
Synonym name:
Catalogue No.: BP0098
Cas No.: 105454-04-4
Formula: C47H51NO14
Mol Weight: 853.918
Botanical Source: From Taxus brevifolia (Taxaceae)
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Can be supplied from milligrams to grams.
For Reference Standard and R&D, Not for Human Use Directly.
Inquire for bulk scale.
Description:
7-Epitaxol is the major derivative of taxol found in cells and taxol (paclitaxel) is a well-known natural-source cancer drug.
References:
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Aug;242(2):692-8.
Taxol is converted to 7-epitaxol, a biologically active isomer, in cell culture medium.
The hydrolysis products of taxol have been isolated by high-performance liquid chromatography and identified by nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectroscopy. In contrast to taxol, the major hydrolysis product, baccatin III, has little cytotoxic activity and does not promote in vitro microtubule assembly.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In cell culture medium, the concentration of taxol decreases with time and 7-Epitaxol, which exhibits properties comparable to those of taxol both on cells and on in vitro microtubuli polymerization, is formed. Baccatin III is found in small quantities in the cell medium, although it is barely detectable within the cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
It is concluded that 7-Epitaxol is the major derivative of taxol found in cells and that its presence does not alter, in a major way, the overall biological activity of taxol.
HPLC of 7-Epitaxol

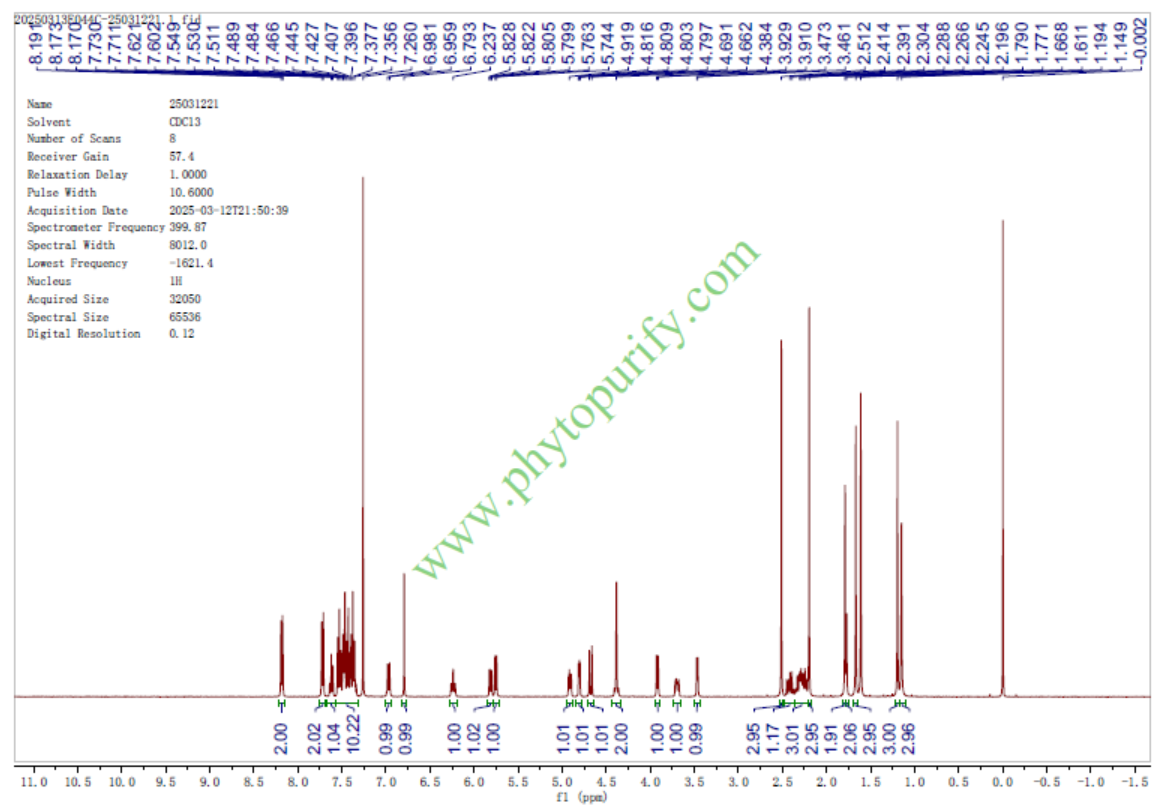
HNMR of 7-Epitaxol