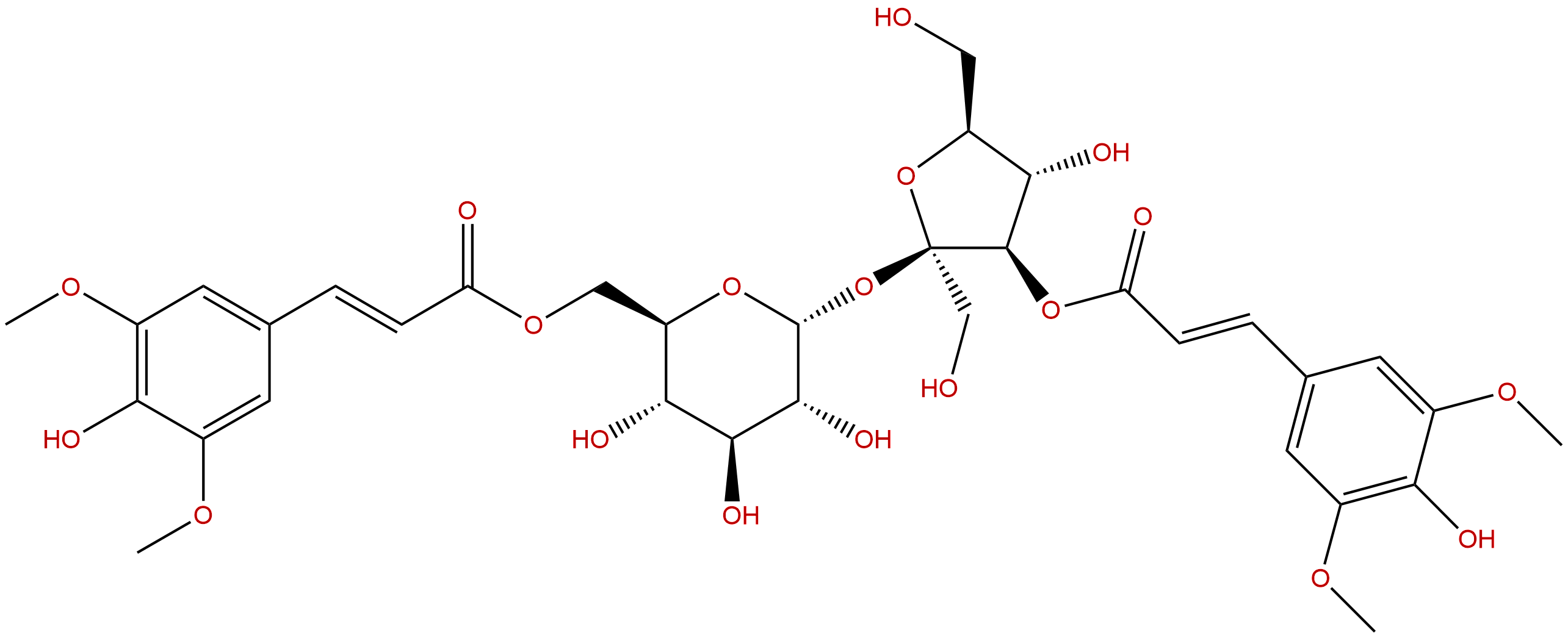
3,6′-Disinapoylsucrose.CAS No.:139891-98-8
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP1629 |
| Formula: | C34H42O19 |
| Mol Weight: | 754.691 |
Product name: 3,6′-Disinapoylsucrose.
Synonym name: 3,6′-Disinapoylsucrose.
Catalogue No.: BP1629
Cas No.: 139891-98-8
Formula: C34H42O19
Mol Weight: 754.691
Botanical Source: " Constit. of Polygala virgata, Polygala reinii, Polygala tenuifolia, Raphanus sativus and Securidaca longipedunculata"
Physical Description: Powder
Type of Compound: Phenylpropanoids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams. Inquire for bulk scale.
We provide solution to improve the water-solubility of compounds, thereby facilitating the variety of activity tests and clinic uses.
For Reference Standard and R&D, Not for Human Use Directly.
Description:
3,6'-Disinapoyl sucrose has neuroprotective effect and antidepressive activity in rats, at least in part, by increasing expression of cyclic AMP response element (CRE)-binding protein (CREB) and its downstream target protein, brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). 3,6'-Disinapoyl sucrose protect neuron cells from glutamate-induced excitotoxicity include the downregulation of proapoptotic gene Bax and the upregulation of antiapoptotic gene Bcl-2.
References:
J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012;2012:1-5.
Protection of SH-SY5Y neuronal cells from glutamate-induced apoptosis by 3,6'-disinapoyl sucrose, a bioactive compound isolated from Radix Polygala.
The neuroprotective effects of 3,6'-Disinapoyl sucrose (DISS) from Radix Polygala against glutamate-induced SH-SY5Y neuronal cells injury were evaluated in the present study.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
SH-SY5Y neuronal cells were pretreated with glutamate (8 mM) for 30 min followed by cotreatment with 3,6'-Disinapoyl sucrose for 12 h. Cell viability was determined by (3,4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenylte-trazolium bromide (MTT) assay, and apoptosis was confirmed by cell morphology and flow cytometry assay, evaluated with propidium iodide dye. Treatment with 3,6'-Disinapoyl sucrose (0.6, 6, and 60 μmol/L) increased cell viability dose dependently, inhibited LDH release, and attenuated apoptosis. The mechanisms by which 3,6'-Disinapoyl sucrose protected neuron cells from glutamate-induced excitotoxicity included the downregulation of proapoptotic gene Bax and the upregulation of antiapoptotic gene Bcl-2.
CONCLUSIONS:
The present findings indicated that 3,6'-Disinapoyl sucrose exerts neuroprotective effects against glutamate toxicity, which might be of importance and contribute to its clinical efficacy for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases.
J Pharm Pharmacol. 2011 Jun;63(6):869-74.
Possible mechanism of the antidepressant effect of 3,6'-disinapoyl sucrose from Polygala tenuifolia Willd.
The present study was designed to observe the effects of 3,6'-Disinapoyl sucrose (DISS), an active oligosaccharide ester component obtained from the roots of Polygala tenuifolia Willd., on behavioral and biochemical aspects of depression induced by chronic mild stress (CMS) in rats. It is the first exploration of the possible association between DISS's antidepressant-like effects and biochemical markers of depression, and involved measuring monoamine oxidase (MAO) activity, cortisol levels, superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity and malondialdehyde (MDA) levels.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Rats were exposed to stressor once daily for consecutive 5 weeks. DISS and a positive control drug, fluoxetine, were administered via gastric intubation to once daily for consecutive 3 weeks from the third week. The results showed that rats subjected to CMS exhibit a reduction in sucrose intake. Conversely, brain MAO-A and MAO-B activity, plasma cortisol levels, and MDA levels were increased, while SOD activity was decreased following CMS exposures. DISS significantly inhibited MAO-A and MAO-B activity and blocked plasma elevated cortisol level, an indicator of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. In addition, DISS increases SOD activity, inhibits lipid peroxidation, and lessens production of MDA.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that DISS may possess potent and rapid antidepressant properties, which are mediated via MAO, the HPA axis and oxidative systems. These antidepressant actions make DISS a potentially valuable drug for the treatment of depression.
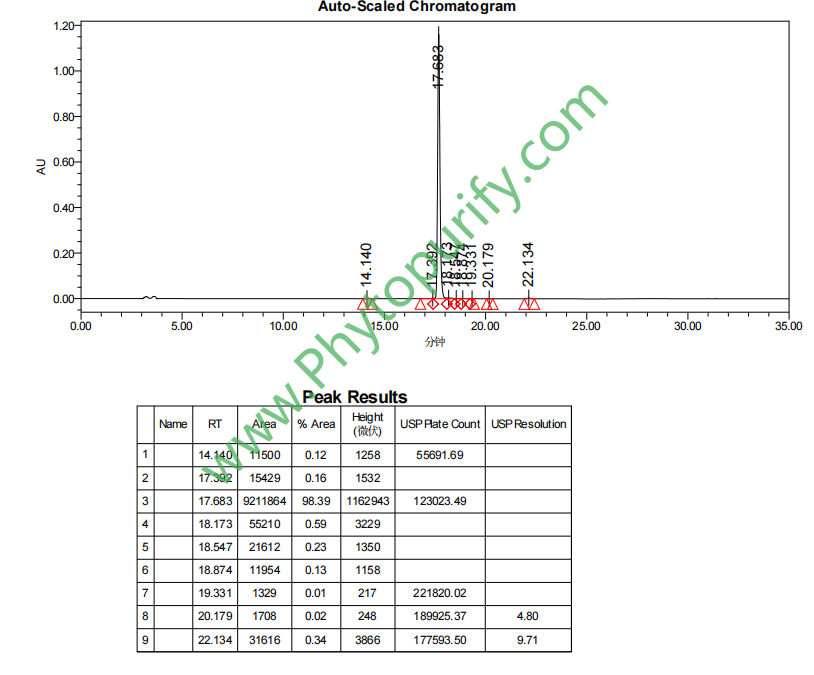
HPLC of 3,6′-Disinapoylsucrose.