
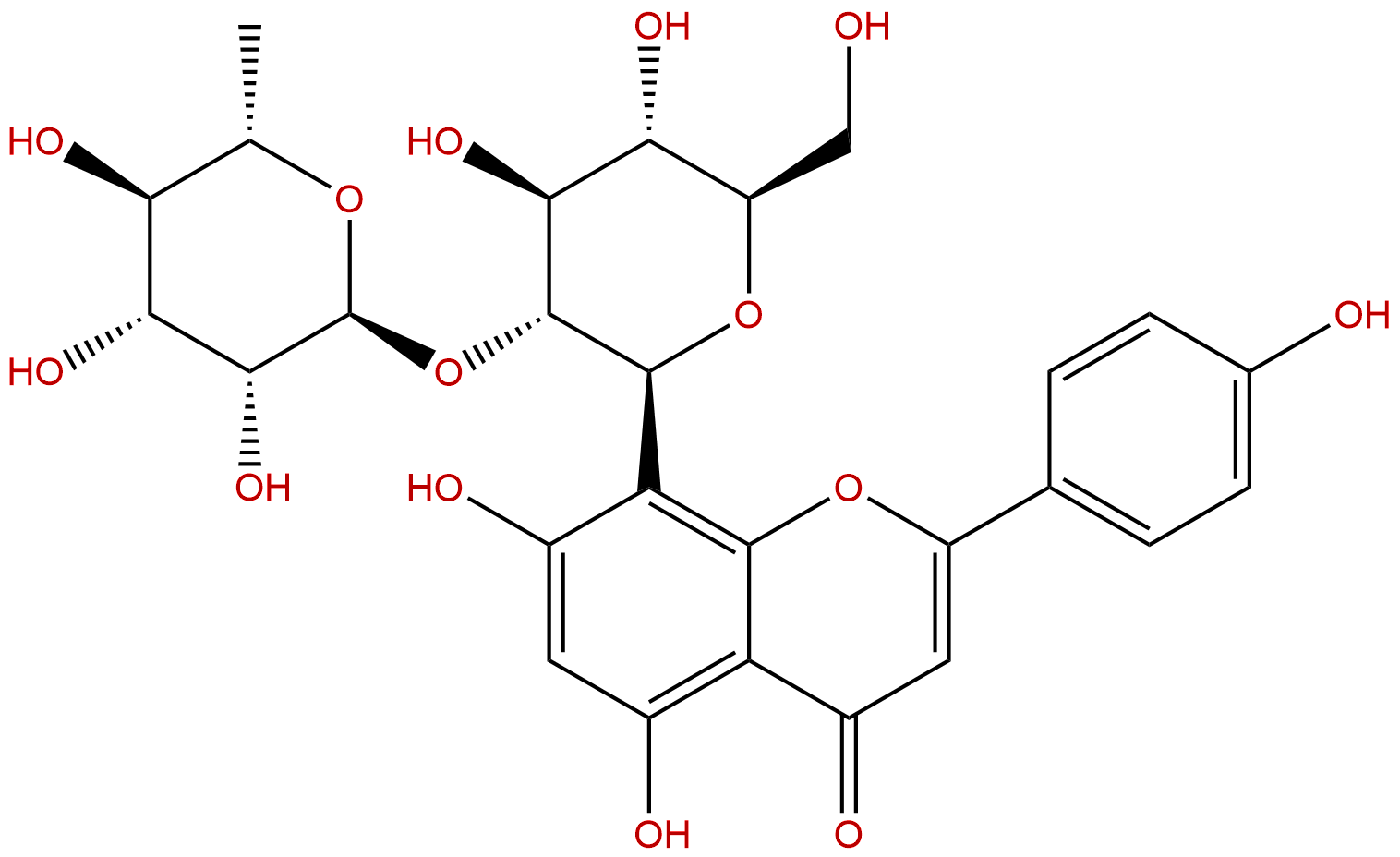
2''-RhamnosylvitexinCAS No.:64820-99-1
|
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0038 |
| Formula: | C27H30O14 |
| Mol Weight: | 578.523 |
Synonym name: Vitexin 2"-o-rhamnoside
Catalogue No.: BP0038
Cas No.: 64820-99-1
Formula: C27H30O14
Mol Weight: 578.523
Botanical Source: Crataegus spp. and other plant spp. Astringent black tea
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Can be supplied from milligrams to grams.
For Reference Standard and R&D, Not for Human Use Directly.
Inquire for bulk scale.
Description:
Vitexin-2''-O-rhamnoside contributes to the protection against H₂O₂ -mediated oxidative stress damage and could be safely used for a wide range of concentrations.It has low bioavailability, mainly related to its poor absorption in the intestine.
References:
J Pharm Pharmacol. 2014 Jul;66(7):988-97.
Effects of vitexin-2"-O-rhamnoside and vitexin-4"-O-glucoside on growth and oxidative stress-induced cell apoptosis of human adipose-derived stem cells.
Vitexin-2''-O-rhamnoside(VOR) and vitexin-4"-O-glucoside (VOG) are the two main flavonoid glycosides of the leaves of Cratagus pinnatifida Bge. var. major N. E. Br. that has been widely used for the treatment of cardiovascular system diseases. In this study, we simultaneously investigated the influence of Vitexin-2''-O-rhamnoside and VOG on human adipose-derived stem cells (hADSCs) injury induced by hydrogen peroxide (H2 O2 ) to further characterize their anti-oxidative and anti-apoptotic activity.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
hADSCs were isolated, cultured in vitro and pretreated with 62.5 μm Vitexin-2''-O-rhamnoside or 120 μm VOG for 24 h and then exposed to 500 μm H2 O2 for an additional 4 h.Pretreatment of hADSCs with Vitexin-2''-O-rhamnoside and VOG was demonstrated to significantly ameliorate the toxicity and apoptosis effects, such as morphological distortion, nuclear condensation, decreased intracellular caspase-3 activity and percentage of cells in apoptosis/necrosis by using morphological assay, immunocytochemistry and flow cytometric evaluation. In addition, Vitexin-2''-O-rhamnoside and VOG caused no cytotoxic effect on hADSCs at concentrations up to 250 and 480 μm, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our results indicated that both Vitexin-2''-O-rhamnoside and VOG contribute to the protection against H2 O2 -mediated oxidative stress damage and could be safely used for a wide range of concentrations.
HPLC of 2"-Rhamnosylvitexin
