
NeohesperidinCAS No.:13241-33-3 |
||||||||||
 |
|
|
||||||||

| Catalogue No.: | BP0991 |
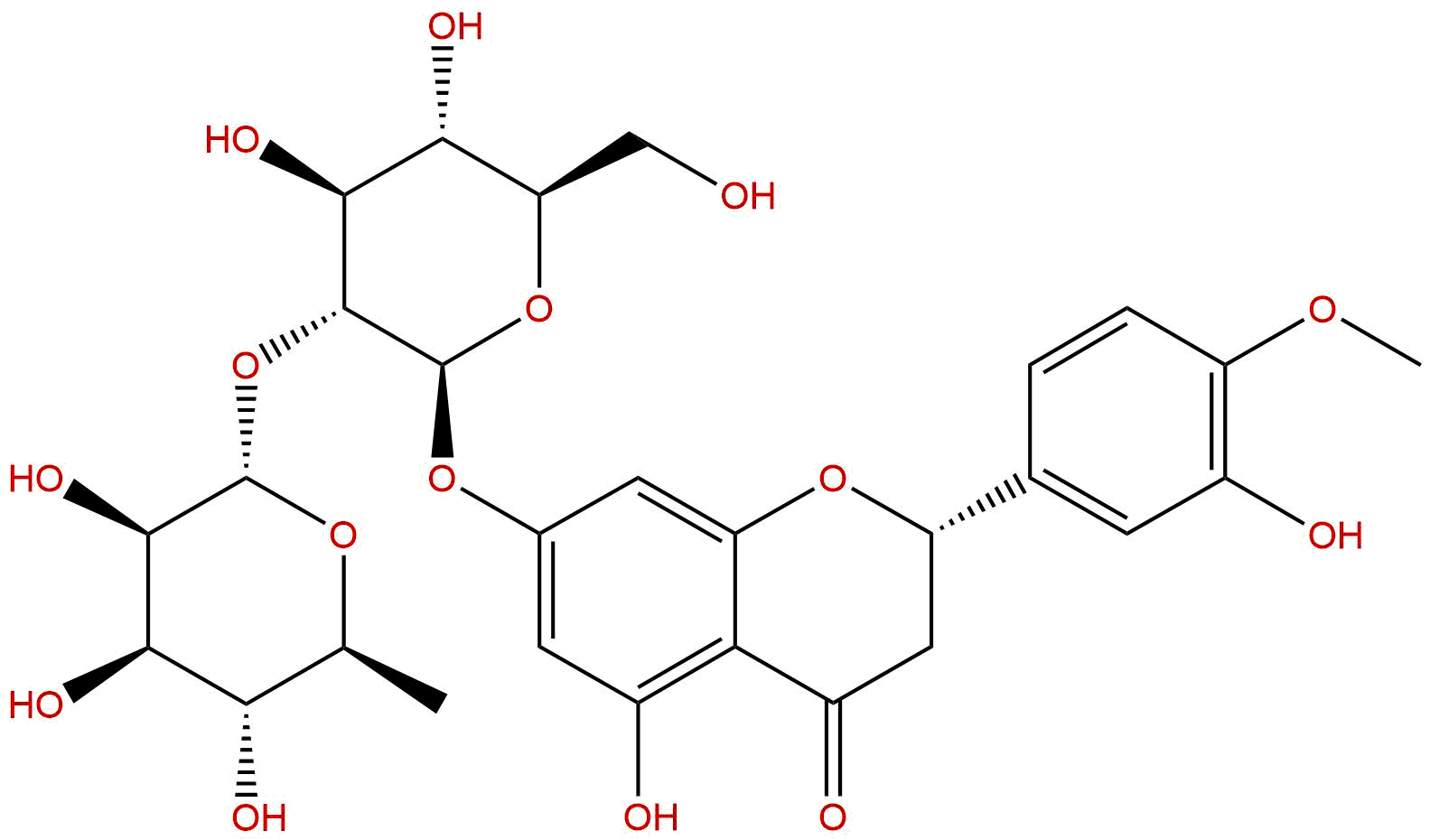
| Formula: | C28H34O15 |
| Mol Weight: | 610.565 |
Product name: Neohesperidin
Synonym name: Hesperetin 7-neohesperidoside
Catalogue No.: BP0991
Cas No.: 13241-33-3
Formula: C28H34O15
Mol Weight: 610.565
Botanical Source: Citrus aurantium and other Citrus spp
Physical Description: Powder
Type of Compound: Flavonoids
Purity: 95%~99%
Analysis Method: HPLC-DAD or/and HPLC-ELSD
Identification Method: Mass, NMR
Packing: Brown vial or HDPE plastic bottle
Storage: Store in a well closed container, protected from air and light. Put into refrigerate or freeze for long term storage.
Whenever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20℃. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks.
The product could be supplied from milligrams to grams, up to kilograms
Inquire for bulk scale.
Descriptions:
Neohesperidin is a natural new nutrition sweetener, widely existing in plants of dry citrus peel, which can be derived from extraction; since the sweetness is 1,300-1,500 times greater than that of sugar, neohesperidin are widely used in fruit juices, wines, beverages, bakeries and pharmaceutical formulations, and are particularly suitable for consumption by diabetic patients.[1]
Neohesperidin exhibits antioxidant activity (IC50=22.31ug/mL) in the 1,1-diphenyl
-2-picryldydrazyl (DPPH) radical-scavenging assay; neohesperidin (50mg/kg) significantly inhibits 55.0% of HCl/ethanol-induced gastric lesions, and increases the mucus content; In pylorus ligated rats, neohesperidin (50 mg/kg) significantly decreases the volume of gastric secretion and gastric acid output, and increases the pH; suggests that neohesperidin isolated from PF may be useful for the treatment and/or protection of gastritis. [2]
Neohesperidin has free radical scavenging activity, can induce cellular apoptosis in human breast adenocarcinoma MDA-MB-231 cells via activating the Bcl-2/Bax-mediated signaling pathway.[3]
Neohesperidin can attenuate cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via the inhibition of neuronal and oxidative stress through the regulation of the apoptotic pathway and activating the Akt/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway.[4]
Neohesperidin and hesperidin are the major flavanones isolated from bittersweet orange, they have potent anti-inflammatory effects in various inflammatory models, they significantly aggravate gastric damage caused by indomethacin administration as evidenced by increased ulcer index and histopathological changes of stomach.[5]
Neohesperidin, Albiflorin, and Aloeemodin have a potent inhibitory effect on Aβ1-40 and Aβ1-42 aggregation, and have neuroprotective effect on primary hippocampal cells against β-Amyloid induced toxicity.[6]
References:
[1] Yang H J, Jeong S Y, Choi N S, et al. ??????, 2010,11, 1691-6.
[2] Lee J H, Lee S H, Kim Y S, et al. Phytother Res, 2009, 23(12):1748–53.
[3] Xu F, Zang J, Chen D, et al. Nat Prod Commun, 2012, 7(11):1475-8.
[4] Wang J J, Cui P. J Asian Nat Prod Res, 2013, 15(9):1023-37.
[5] Hamdan D I, Mahmoud M F, Wink M, et al. Environ Toxicol Phar, 2014, 37(3):907-15.
[6] Ho S L, Poon C Y, Lin C, et al. Curr Alzheimer Res, 2015, 12(5):424-33.
[7] Wang Q H, Gao S H, Xiong X J, et al. Academic Journal of Second Military Medical University, 2015, 36(8):917-21.
HPLC of Neohesperidin
